HashMap作为我们最常用的数据类型,当然有必要了解一下他内部是实现细节。相比于 JDK7 在JDK8 中引入了红黑树以及hash计算等方面的优化,使得 JDK8 中的HashMap效率要高于以往的所有版本,本文会详细介绍相关的优化,但是主要还是写 JDK8 的源码。
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {}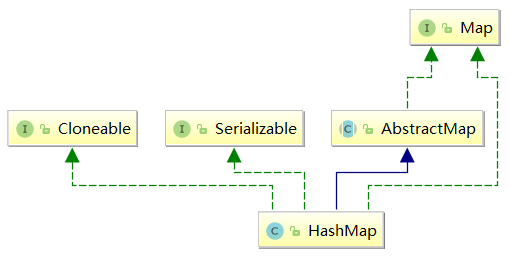
可以看到HashMap是完全基于Map接口实现的,其中AbstractMap是Map接口的骨架实现,提供了Map接口的最小实现。HashMap看名字也能猜到,他是基于哈希表实现的(数组+链表+红黑树):
public HashMap(int initialCapacity)public HashMap()public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}HashMap一共有四个构造函数,其主要作用就是初始化loadFactor和threshold两个参数:
threshold:扩容的阈值,当放入的键值对大于这个阈值的时候,就会发生扩容;
loadFactor:负载系数,用于控制阈值的大小,即threshold = table.length * loadFactor;默认情况下负载系数等于0.75,当它值越大时:哈希桶空余的位置越少,空间利用率越高,同时哈希冲突也就越严重,效率也就越低;相反它值越小时:空间利用率越低,效率越高;而0.75是对于空间和效率的一个平衡,通常情况下不建议修改;
但是对于上面构造函数当中this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);,这里的阈值并没有乘以负载系数,是因为在构造函数当中哈希桶table[]还没有初始化,在往里put数据的时候才会初始化,而tableSizeFor是为了得到大于等于initialCapacity的最小的2的幂;
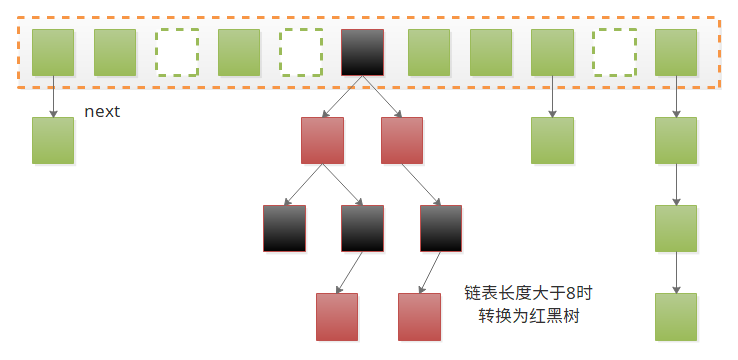
transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 哈希桶transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; // 映射关系Set视图transient int size; // 键值对的数量transient int modCount; // 结构修改次数,用于实现fail-fast机制哈希桶的结构如下:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; // 用于寻址,避免重复计算
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
... public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
}其中Node<K,V> next还有一个TreeNode子类用于实现红黑树,需要注意的是这里的hashCode()所计算的hash值只用于在遍历的时候获取hash值,并非寻址所用hash;
既然是Hash表,那么最重要的肯定是寻址了,在HashMap中采用的是除留余数法,即table[hash % length],但是在现代CPU中求余是最慢的操作,所以人们想到一种巧妙的方法来优化它,即length为2的指数幂时,hash % length = hash & (length-1),所以在构造函数中需要使用tableSizeFor(int cap)来调整初始容量;
/**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16; return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}首先这里要明确:
2的幂的二进制是,1后面全是0
有效位都是1的二进制加1,就可以得到2的幂
以33为例,如图:

因为int是4个字节32位,所以最多只需要将高位的16位与低位的16位做或运算就可以得到2的幂,而int n = cap - 1;是为了避免cap本身就是2的幂的情况;这个算是真是厉害,看了很久才看明白,实在汗颜。
计算 hash
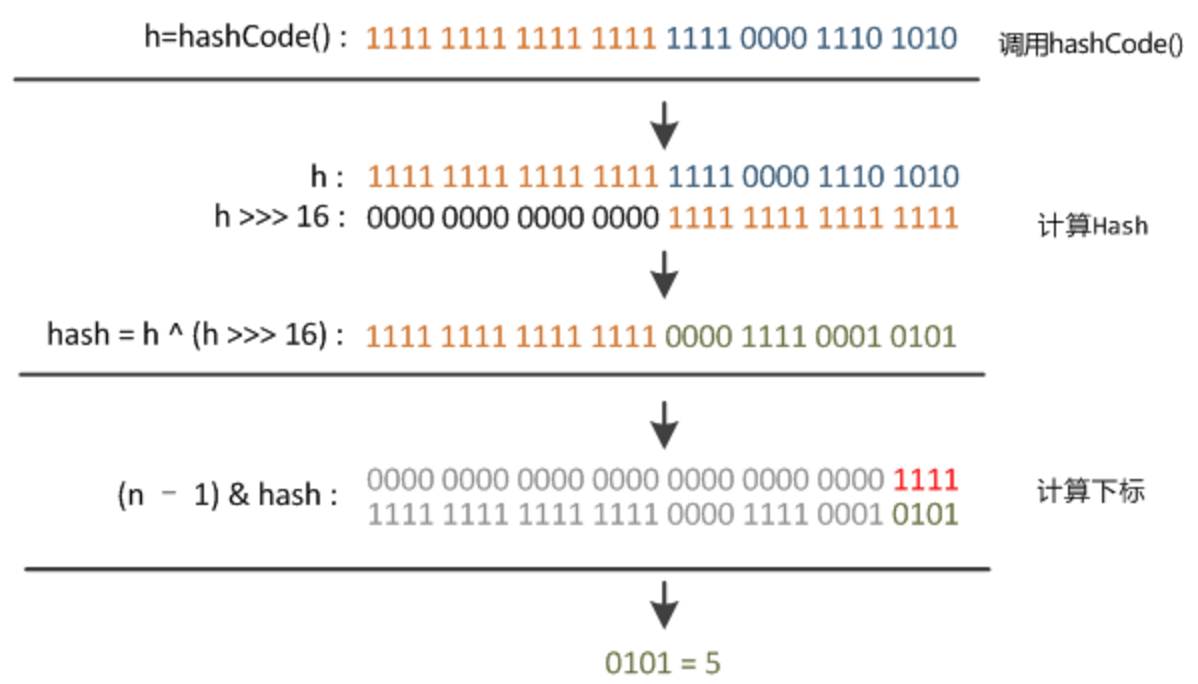
static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}这里重新计算hash是因为在hash & (length-1)计算下标的时候,实际只有hash的低位参与的运算容易产生hash冲突,所以用异或是高位的16位也参与运算,以减小hash冲突,要理解这里首先要明白,
& 操作之后只会保留下都是1的有效位
length-1(2的n次方-1)实际上就是n和1
& 操作之后hash所保留下来的也只有低位的n个有效位,所以实际只有hash的低位参与了运算
具体如图所示:
对于Map而言最重要的当然是Get和Put等操作了,所以下面将介绍与之相关的操作;
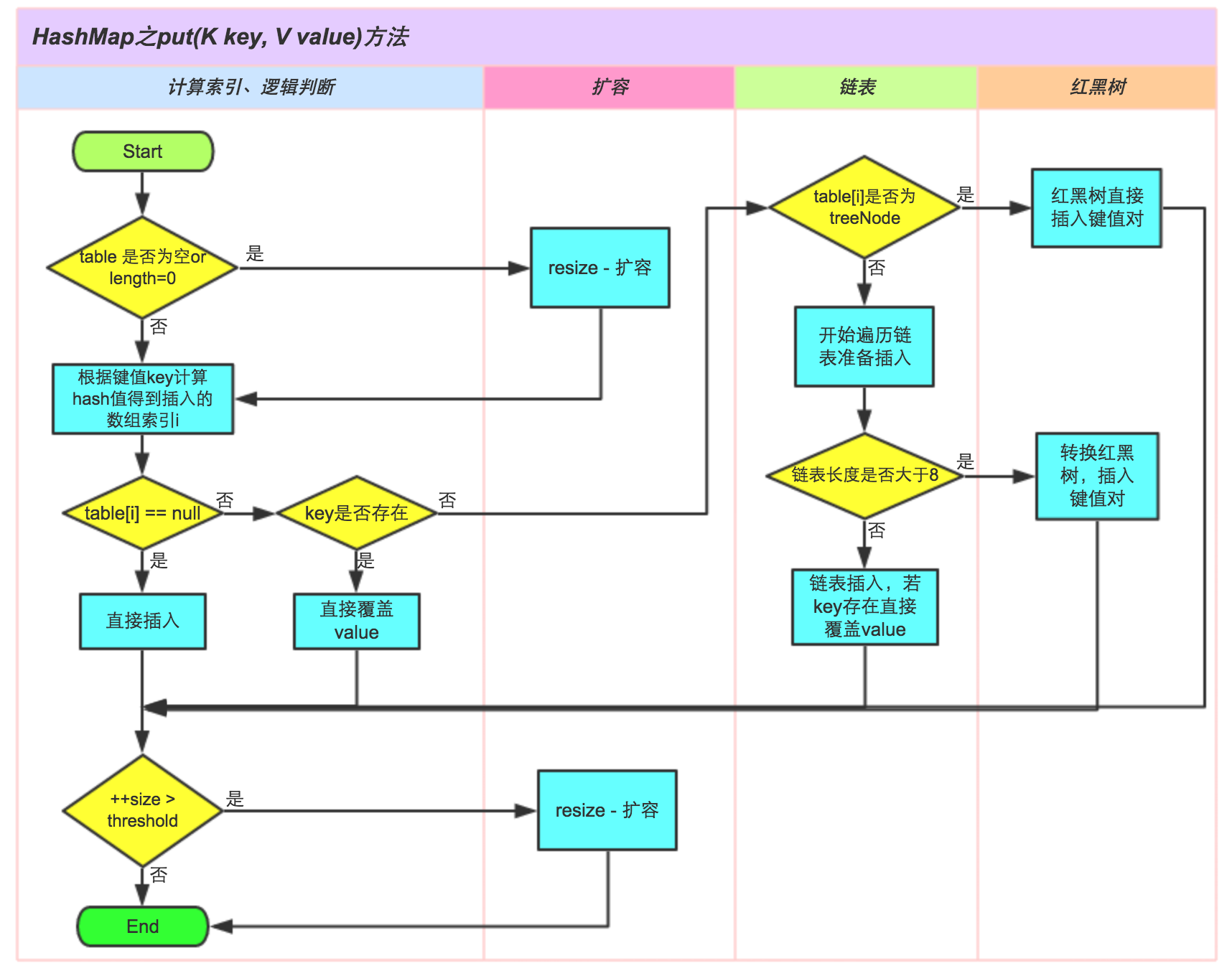
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods * * @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; // 如果没有初始化哈希桶,就使用resize初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length; // 如果hash对应的哈希槽是空的,就直接放入
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else {
Node<K,V> e; K k; // 如果已经存在key,就替换旧值
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p; // 如果已经是树节点,就用putTreeVal遍历树赋值
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { // 遍历链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { // 遍历到最后一个节点也没有找到,就新增一个节点
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 如果链表长度大于8,则转换为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash); break;
} // 找到key对应的节点则跳出遍历
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break;
p = e;
}
} // e是最后指向的节点,如果不为空,说明已经存在key,则替换旧的value
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue;
}
} // 新增节点时结构改变modCount加1
++modCount; if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null;
}具体过程如图所示:
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { // 如果hash桶已经完成初始化,并且已达最大容量,则直接返回
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab;
} // 如果扩大2倍没有超过最大容量,则扩大两倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
} // 如果threshold已经初始化,则初始化容量为threshold
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr; // 如果threshold和哈希桶都没有初始化,则使用默认值
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
} // 重新计算threshold
if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null; // 如果只有一个节点,则直接重新放置节点
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; // 如果是树节点,则将红黑树拆分后,重新放置
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); // 将链表拆分为原位置和高位置两条链表
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next; do {
next = e.next; // 节点重新放置后在原位置
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null)
loHead = e; else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
} // 节点重新放置后位置+oldCap
else { if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e; else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null); // 放置低位置链表
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
} // 放置高位置链表
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
} return newTab
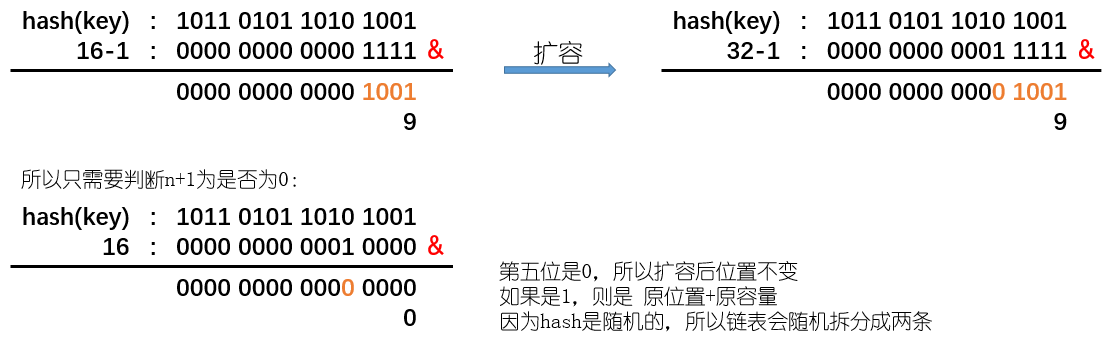
}上面的扩容过程需要注意的是,因为哈希桶长度总是2的幂,所以在扩大两倍之后原来的节点只可能在原位置或者原位置+oldCap,具体判断是通过(e.hash & oldCap) == 0实现的;
之前将了 & 操作只保留了都是1的有效位
oldCap 是2的n次方,实际也就是在n+1的位置为1,其余地方为0
因为扩容是扩大2倍,实际上也就是在hash上取了 n+1位,那么就只需要判断多取的第n+1位是否为0
如图所示:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
} return null;
}相较于其他方法get方法就要简单很多了,只是用hash取到对应的hash槽,在依次遍历即可。
public Object clone() {
HashMap<K,V> result; try {
result = (HashMap<K,V>)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
result.reinitialize();
result.putMapEntries(this, false); return result;
}对于clone方法这里有一个需要注意的地方,result.putMapEntries(this, false),这里在put节点的时候是用的this,所以这只是浅复制,会影响原map,所以在使用的时候需要注意一下;
至于其他方法还有很多,但大致思路都是一致的,大家可以在看一下源码。
| Number Of Records | Java 5 | Java 6 | Java 7 | Java 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 4 ms | 3 ms | 4 ms | 2 ms |
| 100,000 | 7 ms | 6 ms | 8 ms | 4 ms |
| 1,000,000 | 99 ms | 15 ms | 14 ms | 13 ms |
| Number Of Records | Java 5 | Java 6 | Java 7 | Java 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 197 ms | 154 ms | 132 ms | 15 ms |
| 100,000 | 30346 ms | 18967 ms | 19131 ms | 177 ms |
| 1,000,000 | 3716886 ms | 2518356 ms | 2902987 ms | 1226 ms |
| 10,000,000 | OOM | OOM | OOM | 5775 ms |
| Number Of Records | Java 5 | Java 6 | Java 7 | Java 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 17 ms | 12 ms | 13 ms | 10 ms |
| 100,000 | 45 ms | 31 ms | 34 ms | 46 ms |
| 1,000,000 | 384 ms | 72 ms | 66 ms | 82 ms |
| 10,000,000 | 4731 ms | 944 ms | 1024 ms | 99 ms |
| Number Of Records | Java 5 | Java 6 | Java 7 | Java 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 211 ms | 153 ms | 162 ms | 10 ms |
| 100,000 | 29759 ms | 17981 ms | 17653 ms | 93 ms |
| 1,000,000 | 3527633 ms | 2509506 ms | 2902987 ms | 333 ms |
| 10,000,000 | OOM | OOM | OOM | 3970 ms |
从以上对比可以看到 JDK8 的 HashMap 无论 hash 是否均匀效率都要好得多,这里面hash算法的改良功不可没,并且因为红黑树的引入使得它在hash不均匀甚至在所有key的hash都相同的情况,任然表现良好。
扩容需要重排所有节点特别损耗性能,所以估算map大小并给定一个合理的负载系数,就显得尤为重要了。
HashMap 是线程不安全的。
虽然 JDK8 中引入了红黑树,将极端hash的情况影响降到了最小,但是从上面的对比还是可以看到,一个好的hash对性能的影响仍然十分重大,所以写一个好的hashCode()也非常重要。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。