【唠叨】
前面我们讲了精灵贴图、标签、菜单、按钮。感觉似乎少了点什么?UI控件里是不是应该还有一个很重要的控件——编辑框。在手机网游中,启动游戏,过了开场动画后,基本上显示的第一个界面应该就是游戏的登录界面了吧。输入用户名、密码什么的,这些都是需要借助编辑框来实现输入的。点击文本,弹出虚拟键盘,输入账号密码,点击登录。
cocos2dx引擎为我们提供了两类编辑框的控件:
(1)CCTextFieldTTF(基于CCLabelTTF)
(2)CCEditBox(基于CCControlButton)
本节就先讲述一下CCTextFieldTTF吧。
【致谢】
http://gl.paea.cn/contents/ff7cec4ea13b9be4.html
http://blog.csdn.net/crayondeng/article/details/12175367
【小知识】
IME: 是指Input Method Editors,即输入法编辑器。
placeholder:默认显示的内容。即编辑框的输入内容为空时,显示的内容。
默认内容: 当编辑框的输入内容为空时,显示的内容。
输入内容: 使用虚拟键盘,输入到编辑框中的内容。
【Demo下载】
https://github.com/shahdza/Cocos_LearningTest/tree/master/demo_%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E6%A1%86%E4%B9%8B%E4%B8%80CCTextFieldTTF
【3.x】
(1)去掉“CC”
(2)增加 alpha透明度值 :参数中的 Color3B 变为 Color4B
(3)setColor(const ccColor3B&) 改为 setTextColor(const Color4B&)
(4)CCLabelTTF 改为 Label
(4)其他3.x的变化:如触摸事件等等……也随之发生变化
【CCTextFieldTTF】
让我们先看一下CCTextFieldTTF的继承关系:
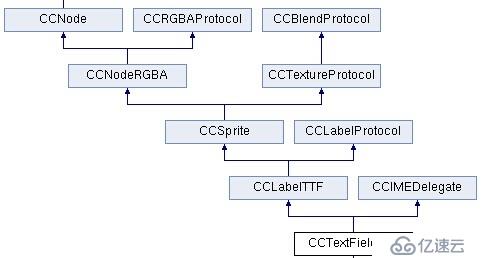
可见,CCTextFieldTTF的父类为:字体标签类CCLabelTTF、输入法代理类CCIMEDelegate。
其中CCLabelTTF之前是讲过的,它是一个用于显示文字的标签类。而CCIMEDelegate这个类主要是为子类提供了虚拟键盘的输入功能。
根据其继承关系,我们大致也可以猜测到CCTextFieldTTF是怎么实现的吧?这个估计就是一个动态的 CCLabelTTF ,通过不断监听输入的字符,动态设置标签的内容。
接下来就来讲讲它的使用方法吧!
1、创建方式
注意:CCTextFieldTTF的创建不是使用create,而是textFieldWithPlaceHolder。
//
class CC_DLL CCTextFieldTTF : public CCLabelTTF, public CCIMEDelegate
/**
* 创建CCTextFieldTTF的两种方式
* textFieldWithPlaceHolder
*/
//placeholder:默认内容。即输入为空时显示的内容。
//fontName: 字体资源名。
//fontSize: 字体大小。
//编辑框的大小为:CCLabelTTF的大小。且在输入的过程中,若内容超过编辑框的大小,会自动扩展。
static CCTextFieldTTF* textFieldWithPlaceHolder(const char* placeholder, const char* fontName, float fontSize);
//placeholder:默认内容。即编辑框的输入内容为空时,显示的内容。
//dimensions: 编辑框的尺寸大小。
//alignment: 文本内容的对齐方式。
//kCCTextAlignmentLeft 左对齐
//kCCTextAlignmentCenter 居中,默认方式
//kCCTextAlignmentRight 右对齐
//编辑框的大小固定,不可扩展。
static CCTextFieldTTF* textFieldWithPlaceHolder(const char* placeholder, const CCSize& dimensions, CCTextAlignment alignment, const char*fontName, float fontSize);
/**
* 创建方式举例
*/
CCTextFieldTTF::textFieldWithPlaceHolder("Please Click Me!", "Marker Felt", 24);
CCTextFieldTTF::textFieldWithPlaceHolder("Please Click Me!", CCSizeMake(100,100), CCTextAlignment::kCCTextAlignmentCenter, "Marker Felt", 24);
//2、常用操作
委托代理对象、字符个数、默认内容及字体颜色、输入内容及字体颜色。
// /** * 属性设置 * setDelegate , getCharCount , * setPlaceHolder , setColorSpaceHolder , * setString , setColor */ //设置编辑框的委托代理对象,一般为this //并且CCLayer必需要继承代理接口类CCTextFieldDelegate。 CC_SYNTHESIZE(CCTextFieldDelegate*, m_pDelegate, Delegate); //获取字符个数,只读get CC_SYNTHESIZE_READONLY(int, m_nCharCount, CharCount); //设置编辑框默认内容。即输入为空时显示的内容 virtual void setPlaceHolder(const char * text); virtual const char* getPlaceHolder(); //设置编辑框默认内容的字体颜色 virtual void setColorSpaceHolder(const ccColor3B& color); virtual const ccColor3B& getColorSpaceHolder(); //设置编辑框输入内容 virtual void setString(const char *text); virtual const char* getString(); //设置编辑框输入内容的字体颜色 virtual void setColor(const ccColor3B& color); virtual const ccColor3B& setColor(); //
3、父类CCIMEDelegate向子类提供的函数
实现虚拟键盘的输入功能。
// virtual bool attachWithIME(); //开启虚拟键盘,并允许输入。 virtual bool detachWithIME(); //关闭虚拟键盘,并停止输入。 //textFieldTTF->attachWithIME(); //
4、事件委托代理接口类CCTextFieldDelegate
CCTextFieldDelegate类主要是用来侦听CCTextFieldTTF的使用状态,并设置事件的回调响应函数。
使用方法:在创建CCTextFieldTTF类的CCLayer类中,让CCLayer继承CCTextFieldDelegate,并重写如下四个事件回调响应函数。
// //当用户启动虚拟键盘时的回调函数 //启用键盘false; 不启用键盘true virtual bool onTextFieldAttachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender) //当用户关闭虚拟键盘时的回调函数 //关闭键盘false; 不关闭键盘true virtual bool onTextFieldDetachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender) //当用户输入时的回调函数 //允许输入字符false; 不允许输入字符true virtual bool onTextFieldInsertText(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* text, int nLen) //当用户删除文字时的回调函数 //允许删除字符false; 不允许删除字符true virtual bool onTextFieldDeleteBackward(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* delText, int nLen) //
5、使用技巧
(1)创建CCTextFieldTTF后,设置编辑框的委托代理对象为当前CCLayer层,即setDelegate(this)。只有这样,继承于CCTextFieldDelegate的CCLayer就可以响应编辑框的事件,并执行回调函数。
(2)通过通过触碰事件Touch,判断触点是否触碰到编辑框内部,来决定是否开启虚拟键盘。触碰到内部,就开启;触碰到外部,就关闭。
(3)通过重写CCTextFieldDelegate的四个回调函数,来对编辑框的不同状态事件进行处理。
【代码实战】
(1)让HelloWorld类继承cocos2d::CCTextFieldDelegate,重写事件侦听函数。并在HelloWorld类中开启触控事件。
记得在onEnter和onExit中注册和注销触控事件哦!
//
class HelloWorld : public cocos2d::CCLayer,cocos2d::CCTextFieldDelegate
{
virtual bool onTextFieldAttachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender); //当用户启动虚拟键盘的时候的回调函数
virtual bool onTextFieldDetachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender); //当用户关闭虚拟键盘的时候的回调函数
virtual bool onTextFieldInsertText(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* text, int nLen); //当用户输入的时候的回调函数
virtual bool onTextFieldDeleteBackward(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* delText, int nLen); //当用户删除文字的时候的回调函数
//开启触控
virtual bool ccTouchBegan(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event);
virtual void ccTouchMoved(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event);
virtual void ccTouchEnded(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event);
virtual void onEnter();
virtual void onExit();
};
//
(2)在init()中创建编辑框CCTextFieldTTF,并给与Tag标记为tag = 1。
//
CCTextFieldTTF* textFieldTTF = CCTextFieldTTF::textFieldWithPlaceHolder("please input", "Marker Felt", 24);
//CCTextFieldTTF* textFieldTTF = CCTextFieldTTF::textFieldWithPlaceHolder("please input", CCSize(100,100), CCTextAlignment::kCCTextAlignmentCenter, "Arial", 20);
textFieldTTF->setPosition( midPos );
this->addChild(textFieldTTF, 0, 1); //tag标记1
//设置编辑框的委托代理对象
textFieldTTF->setDelegate(this);
//
(3)编写触控事件回调函数。根据触点位置,判断开启或关闭虚拟键盘的输入功能。
//
bool HelloWorld::ccTouchBegan(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event)
{
CCLOG("ccTouchBegan");
return true;
}
void HelloWorld::ccTouchMoved(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event)
{
CCLOG("ccTouchMoved");
}
void HelloWorld::ccTouchEnded(CCTouch* touch, CCEvent* event)
{
CCLOG("ccTouchEnded");
//获取触点
CCPoint pos = touch->getLocation();
//获取textFieldTTF所在的矩形区域rect
CCTextFieldTTF* textFieldTTF = (CCTextFieldTTF*)this->getChildByTag(1);
float x = textFieldTTF->getPositionX() - textFieldTTF->getContentSize().width/2;
float y = textFieldTTF->getPositionY() - textFieldTTF->getContentSize().height/2;
float width = textFieldTTF->getContentSize().width;
float height = textFieldTTF->getContentSize().height;
CCRect rect = CCRectMake(x, y, width, height);
//判断触点是否触摸到编辑框内部
if( rect.containsPoint(pos) ) {
CCLOG("attachWithIME");
textFieldTTF->attachWithIME(); //开启虚拟键盘
}else {
CCLOG("detachWithIME");
textFieldTTF->detachWithIME(); //关闭虚拟键盘
}
}
//
(4)编写编辑框事件的回调函数。
当启用虚拟键盘,开始输入时,放大字体大小,并改变字体颜色。
当关闭虚拟键盘,停止输入时,还原字体大小,并改变字体颜色。
//
//当用户启动虚拟键盘的时候的回调函数
bool HelloWorld::onTextFieldAttachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender)
{
//事件处理
sender->setFontSize(30); //字体放大为30
sender->setColor(ccYELLOW); //内容颜色: ***
sender->setColorSpaceHolder(ccWHITE); //默认内容颜色: 白色
return false; //启用键盘。若不启用键盘return true;
}
//当用户关闭虚拟键盘的时候的回调函数
bool HelloWorld::onTextFieldDetachWithIME(CCTextFieldTTF* sender)
{
//事件处理
sender->setFontSize(24); //字体大小还原为24
sender->setColor(ccORANGE); //内容颜色: 橘黄
sender->setColorSpaceHolder(ccGRAY); //默认内容颜色: 灰色
return false; //关闭键盘。若不关闭键盘return true;
}
//当用户输入的时候的回调函数
bool HelloWorld::onTextFieldInsertText(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* text, int nLen)
{
//事件处理
CCLOG("CharCount: %d", sender->getCharCount());
return false; //输入字符。若不允许输入字符return true;
}
//当用户删除文字的时候的回调函数
bool HelloWorld::onTextFieldDeleteBackward(CCTextFieldTTF* sender, const char* delText, int nLen)
{
return false; //删除字符。若不允许删除字符return true;
}
// 运行结果:
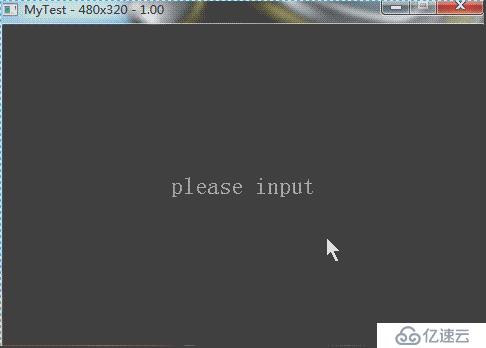
分析与总结:
(1)若编辑框中未输入任何字符时,文本显示的是默认内容“please input”。而当编辑框中有输入内容时,文本显示的是输入内容。
(2)编辑框的尺寸大小,会根据输入的内容大小,自动进行扩展。
(3)输入内容后,可以通过回车键(Enter)结束输入。可以通过回退键(BackSpace)删除字符。
(4)最最关键的问题是:说好的虚拟键盘呢?为什么是用电脑键盘输入的 。好吧,因为Win32没有虚拟键盘,要是想看虚拟键盘的效果,就需要移植到手机上。
。好吧,因为Win32没有虚拟键盘,要是想看虚拟键盘的效果,就需要移植到手机上。
手机上的运行截图如下:




看到虚拟键盘,是不是很激动呀激动呀!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。