本篇算一个资料整理,就是二叉树遍历方法,有先序遍历(PreOrder)、中序遍历(InOrder)、后序遍历(PostOrder)、广度优先遍历二叉树(breadth_first_search)、深度优先遍历(depth_first_search)
示例遍历二叉树: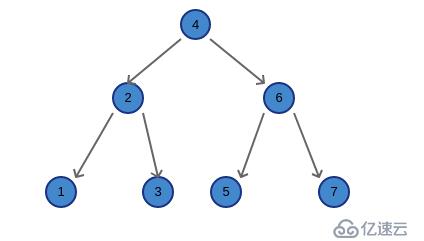
二叉树节点格式:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = self.right = None先遍历根节点,再遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树
def pre_order(root: TreeNode) -> list:
if not root:
return []
return [root.val] + pre_order(root.left) + pre_order(root.right)
#### 遍历结果
## [4, 2, 1, 3, 6, 5, 7]先遍历左子树,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树,
def in_order(root: TreeNode) -> list:
if not root:
return []
return in_order(root.left) + [root.val] + in_order(root.right)
#### 遍历结果
## [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点
def post_order(root: TreeNode) -> list:
if not root:
return []
return post_order(root.left) + post_order(root.right) + [root.val]
#### 遍历结果
## [1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 6, 4]按照层级遍历二叉树
import collections
def breadth_first_search(root: TreeNode) -> list:
"""
这个只是二叉树的广度优先遍历,和图的广度优先不同,返回二叉树的遍历顺序
:param root: TreeNode
:return: list
"""
if not root:
return []
queue = collections.deque() # 申请一个双端队列
queue.append(root)
result = []
# visited = set(root) # 因为是树的结构,所以只要向下走不会存在重复的情况
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft() # 这里从左边出了,下面加入的时候就要加到末尾,若是从右边出,则下面从左边push进去
result.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return result
### 输出结果
## [4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 7]是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。 沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。 当节点v的所在边都己被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。 这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止
def depth_first_search(root: TreeNode, result=[]) -> list:
"""
二叉树广度优先遍历,返回广度遍历顺序
:param root:
:param result:
:return:
"""
if not root:
return []
result.append(root.val)
depth_first_search(root.left, result)
depth_first_search(root.right, result)
return result
### 输出结果
## [4, 2, 1, 3, 6, 5, 7]免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。