前言
@Conditional是Spring4新提供的注解,它的作用是根据某个条件创建特定的Bean,通过实现Condition接口,并重写matches接口来构造判断条件。总的来说,就是根据特定条件来控制Bean的创建行为,这样我们可以利用这个特性进行一些自动的配置。
本文将分为三大部分,@Conditional源码的介绍、Condition的使用示例和@Conditional的扩展注解的介绍。
一、@Conditional的源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* All {@link Condition Conditions} that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
* in order for the component to be registered.
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}从源码中可以看到,@Conditional注解可以用在类和方法上,需要传入一个实现了Condition接口class数组。
二、代码示例
下面将以不同的操作系统为条件,通过实现Condition接口,并重写其matches方法来构造判断条件。若在Windows系统下运行程序,则输出列表命令为dir;若在Linux系统下运行程序,则输出列表命令为ls。
1.判断条件类的定义
(1).判断Windows的条件
package com.study.day01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name").contains("Windows");
}
}(2).判断Linux的条件
package com.study.day01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name").contains("Linux");
}
}2.不同系统下的Bean的类
(1).接口代码
package com.study.day01;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public interface ListService {
public String showListCmd();
}(2).Windows实现类代码
package com.study.day01;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public class WindowsService implements ListService {
public String showListCmd() {
return "dir";
}
}(3).Linux实现类代码
package com.study.day01;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public class LinuxService implements ListService {
public String showListCmd() {
return "ls";
}
}3.配置类
package com.study.day01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class Config {
@Bean
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
public ListService window() {
return new WindowsService();
}
@Bean
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)
public ListService linux() {
return new LinuxService();
}
}4.运行类
package com.study.day01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @Auther: lifq
* @Description:
*/
public class Main01 {
public static void main (String []args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
ListService listService = applicationContext.getBean(ListService.class);
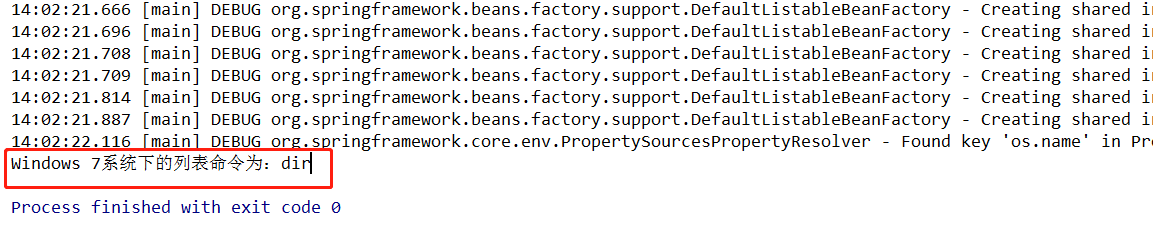
System.out.println(applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name") + "系统下的列表命令为:" + listService.showListCmd());
}
}我的是Windows操作系统,输出结果为dir,运行截图如下:
运行截图
@Conditional注解例子演示完成,有问题欢迎留言沟通哦!
完整源码地址:https://github.com/suisui2019/springboot-study
三、@Conditional的扩展注解
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对亿速云的支持。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。