这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关异常处理在Java中的作用有哪些,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
2、Java程序在执行过程中所发生对异常事件可分为两类:
3、运行时异常和编译时异常
运行时异常
编译时异常
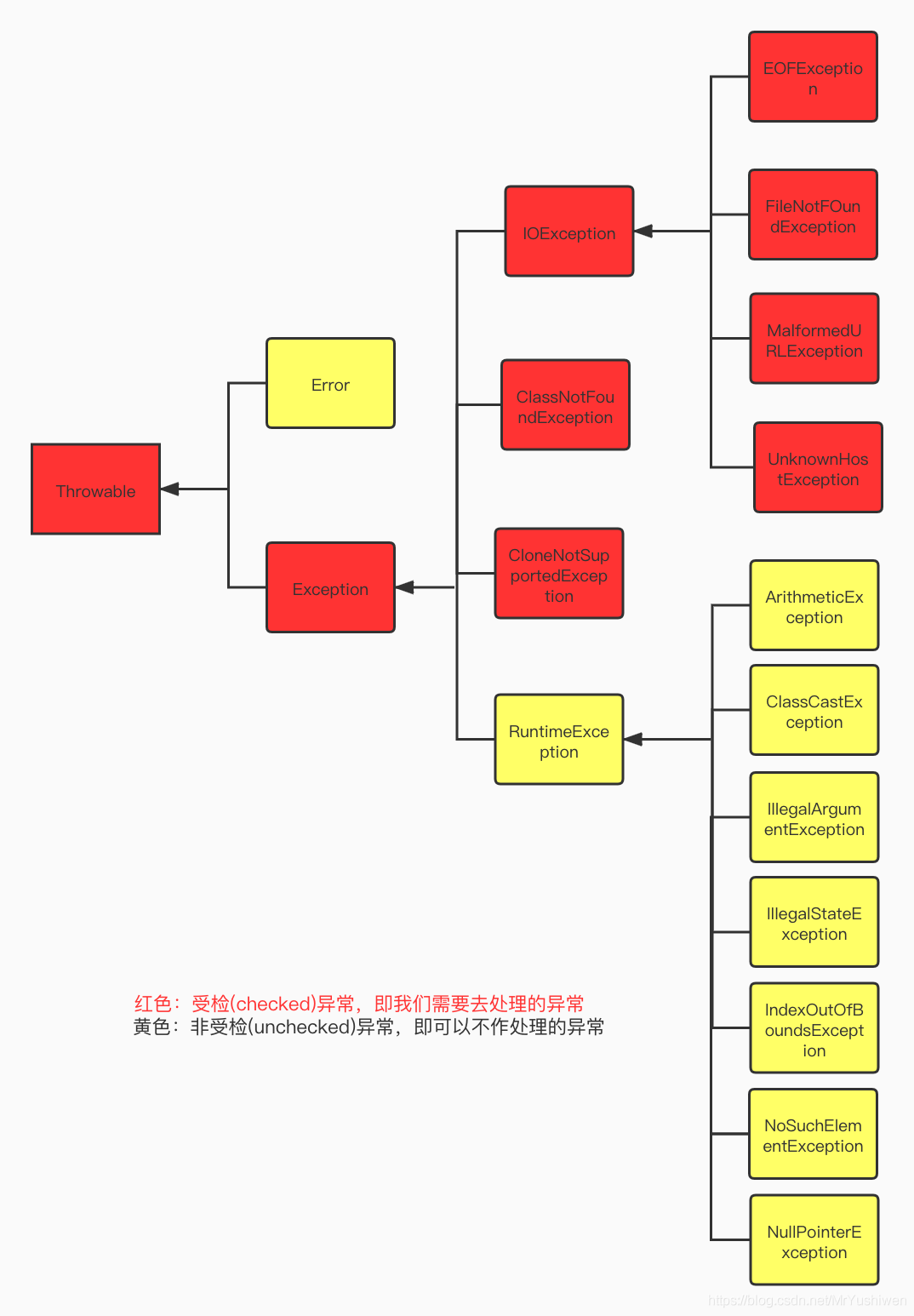
代码示例一:java.lang.OutOfMemoryError(堆溢出)
public class ErrorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//堆溢出:java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
Long[] arr = new Long[1024*1024*1024];
}
}运行结果:
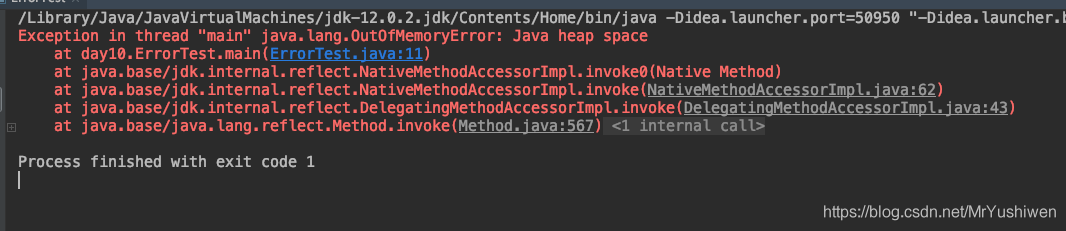
代码示例二:java.lang.StackOverflowError(栈溢出)
public class ErrorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//栈溢出:java.lang.StackOverflowError
main(args);
}
}运行结果:
2.Exception(运行时异常和编译时异常)
运行时异常
/* ******************以下是运行时异常****************** */
//ArithmeticException
@Test
public void test1(){
int num1 = 3;
int num2 = 0;
int num3 = 3 / 0;
}
//InputMismatchException
@Test
public void test2(){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(i);
scanner.close();
}
//NumberFormatException
@Test
public void test3(){
String str = "abcd";
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
}
//ClassCastException
@Test
public void test4(){
Object obj = new Boolean(true);
String str = (String)obj;
}
//IndexOutOfBoundsException
@Test
public void test5(){
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Byte[] bytes = new Byte[3];
System.out.println(bytes[4]);
}
//NullPointerException
@Test
public void test6(){
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[1]);
}编译时异常
/* ******************以下是编译时异常****************** */
@Test
public void test7(){
File file = new File("a.txt");
//java.io.FileNotFoundException
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//java.io.IOException
int date = fis.read();
while (date != -1){
System.out.println((char)date);
date = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
}ps:对于编译时异常,我们需要异常处理
过程一:“抛”:程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象, 并将此对象抛出;一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不再执行。
关于异常对象的产生:
① 系统自动生成的异常对象
② 手动的生成一个异常对象,并抛出(throw)
过程二:“抓”:可以理解为异常的处理方式:① try-catch-finally ② throws
try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
//处理异常的方式1
}catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
//处理异常的方式2
}catch(异常类型3 变量名3){
//处理异常的方式3
}
…
finally{
//一定会执行的代码
}说明:
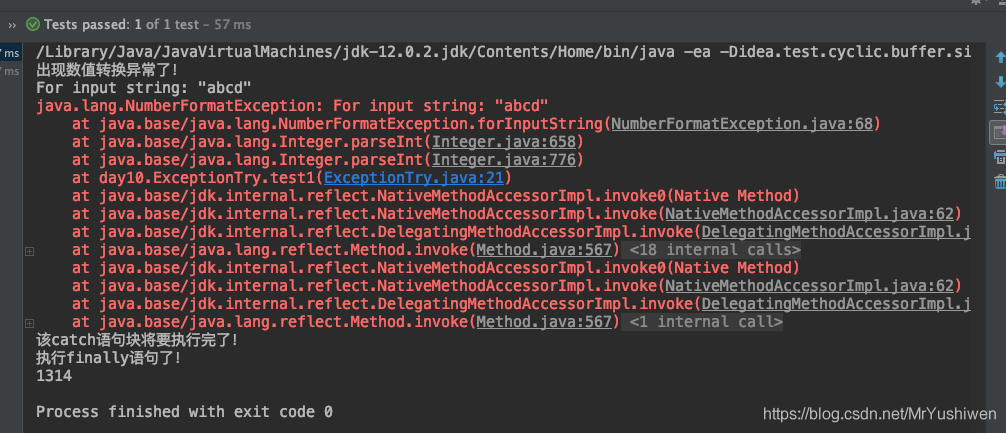
示例一:
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "abcd";
int num = 1314;
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("进入try代码块!");
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("出现数值转换异常了!");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("该catch语句块将要执行完了!");
} catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("出现空指针异常!");
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了");
}finally {
System.out.println("执行finally语句了!");
}
System.out.println(num);
}输出结果:
示例二:
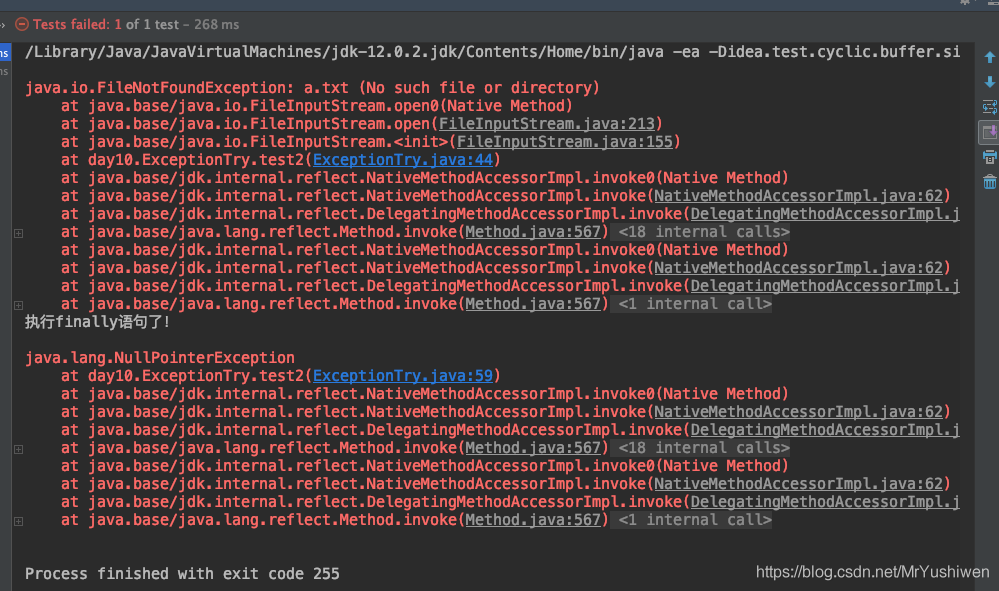
@Test
public void test2(){
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int date = fis.read();
while(date != -1){
System.out.println((char)date);
date = fis.read();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("执行finally语句了!");
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出结果:
总结:
"throws + 异常类型"写在方法的声明处。指明此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型。一旦当方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足throws后异常类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码,就不再执行!
try-catch-finally:真正的将异常给处理掉了。
throws的方式只是将异常抛给了方法的调用者。 并没有真正将异常处理掉。
子类重写的方法抛出的异常类型不大于父类被重写的方法抛出的异常类型(子类重写的方法也可以不抛出异常)
public class SuperClass {
public void method() throws IOException {
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
//报错,子类重写的方法抛出的异常类型不大于父类被重写的方法抛出的异常类型
// public void method() throws Exception{
//
// }
public void method() throws FileNotFoundException{
}
}开发中如何选择使用try-catch-finally 还是使用throws? 如果父类中被重写的方法没有throws方式处理异常,则子类重写的方法也不能使用throws,意味着如果
子类重写的方法中有异常,必须使用try-catch-finally方式处理。执行的方法a中,先后又调用了另外的几个方法,这几个方法是递进关系执行的。我们建议这几个方法使用throws
的方式进行处理。而执行的方法a可以考虑使用try-catch-finally方式进行处理。
代码示例:
public class ErrorThrows {
public static void method1() throws IOException {
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
int data = fileInputStream.read();
while(data != -1){
System.out.println((char)data);
data = fileInputStream.read();
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
public static void method2() throws IOException {
method1();
}
public static void method3() throws IOException {
method1();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method3();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}代码示例:
public class ReturnException {
static void method1(){
try{
System.out.println("进入方法1");
throw new RuntimeException("手动抛出异常");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("执行finally语句了!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
}输出结果:

自定义异常类,有如下三步骤:
自定义异常类:
public class MyExceptionClass extends Exception{
static final long serialVersionUID = -5641210210148784L;
public MyExceptionClass() {
}
public MyExceptionClass(String message) {
super(message);
}
}手动抛出上述自定义的异常类对象:
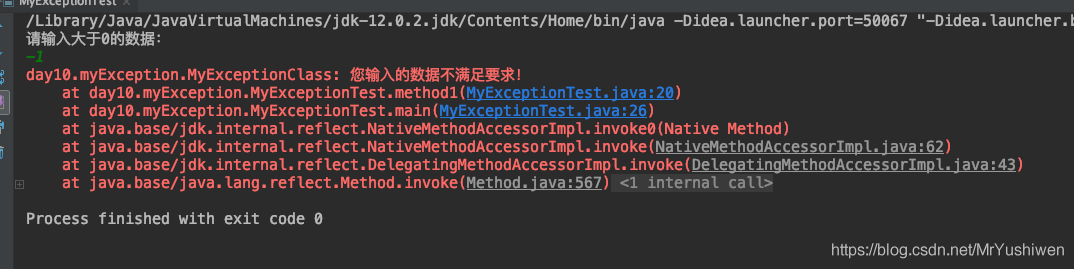
public class MyExceptionTest {
static void method1() throws MyExceptionClass {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入大于0的数据:");
double next = scanner.nextDouble();
if(next >0){
System.out.println("您输入的数据为:"+next);
}else {
throw new MyExceptionClass("您输入的数据不满足要求!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method1();
} catch (MyExceptionClass myExceptionClass) {
myExceptionClass.printStackTrace();
}
}
}运行结果:
关于异常处理在Java中的作用有哪些就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。