这篇文章给大家介绍leetcode中怎么利用多线程实现按序打印,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
我们提供了一个类:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三个不同的线程 A、B、C 将会共用一个 Foo 实例。一个将会调用 first() 方法
一个将会调用 second() 方法
还有一个将会调用 third() 方法
请设计修改程序,以确保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被执行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被执行。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3]
输出: "firstsecondthird"
解释:
有三个线程会被异步启动。
输入 [1,2,3] 表示线程 A 将会调用 first() 方法,线程 B 将会调用 second() 方法,线程 C 将会调用 third() 方法。
正确的输出是 "firstsecondthird"。
示例 2:输入: [1,3,2]
输出: "firstsecondthird"
解释:
输入 [1,3,2] 表示线程 A 将会调用 first() 方法,线程 B 将会调用 third() 方法,线程 C 将会调用 second() 方法。
正确的输出是 "firstsecondthird"。
提示:
尽管输入中的数字似乎暗示了顺序,但是我们并不保证线程在操作系统中的调度顺序。
你看到的输入格式主要是为了确保测试的全面性。
package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 按序打印-实现方案1-锁
*
我们提供了一个类:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三个不同的线程 A、B、C 将会共用一个 Foo 实例。
一个将会调用 first() 方法
一个将会调用 second() 方法
还有一个将会调用 third() 方法
请设计修改程序,以确保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被执行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被执行。
*
*
*/
class Foo {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition firstCondition = lock.newCondition();
final Condition secondCondition = lock.newCondition();
final Condition thirdCondition = lock.newCondition();
private volatile int flag = 0;
public void first() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 0) {
firstCondition.await();
}
print("first");
flag = 1;
secondCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void second() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 1) {
secondCondition.await();
}
print("second");
flag = 2;
thirdCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void third() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 2) {
thirdCondition.await();
}
print("third");
flag = 0;
firstCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo foo = new Foo();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 按序打印-实现方案2-传统方式
*
我们提供了一个类:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三个不同的线程 A、B、C 将会共用一个 Foo 实例。
一个将会调用 first() 方法
一个将会调用 second() 方法
还有一个将会调用 third() 方法
请设计修改程序,以确保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被执行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被执行。
*
*
*/
class Foo2 {
private volatile int flag = 0;
public synchronized void first() {
try {
while(this.flag != 0) {
this.wait();
}
print("first");
flag = 1;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void second() {
try {
while(this.flag != 1) {
this.wait();
}
print("second");
flag = 2;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void third() {
try {
while(this.flag != 2) {
this.wait();
}
print("third");
flag = 0;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo2 foo = new Foo2();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* 按序打印-实现方案3-信号量
*
我们提供了一个类:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三个不同的线程 A、B、C 将会共用一个 Foo 实例。
一个将会调用 first() 方法
一个将会调用 second() 方法
还有一个将会调用 third() 方法
请设计修改程序,以确保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被执行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被执行。
*
*
*/
class Foo3 {
private final Semaphore firstSp = new Semaphore(1);
private final Semaphore secondSp = new Semaphore(0);
private final Semaphore thirdSp = new Semaphore(0);
public void first() {
try {
firstSp.acquire();
print("first");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
secondSp.release();
}
}
public void second() {
try {
secondSp.acquire();
print("second");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
thirdSp.release();
}
}
public void third() {
try {
thirdSp.acquire();
print("third");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
firstSp.release();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo3 foo = new Foo3();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}打印设置:
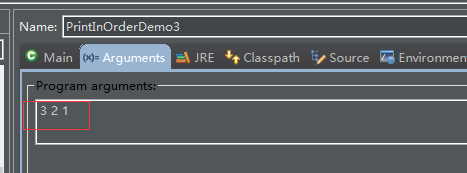
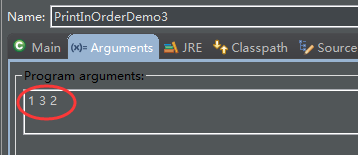
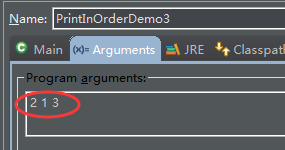
输出:
firstsecondthird
关于leetcode中怎么利用多线程实现按序打印就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/Howard2016/blog/5017958