本篇内容主要讲解“.net core静态中间件有什么作用”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“.net core静态中间件有什么作用”吧!
我们使用静态文件调用:
app.UseStaticFiles();
那么这个默认会将我们根目录下的wwwroot作为静态目录。
这个就比较值得注意的,可能刚开始学.net core 的小伙伴,会直接把脚本写在更目录script这样是访问不到的。
当然了,你可以配置参数。可以给UseStaticFiles传递参数。不过建议不要这么干,因为这是一种默认的约定。
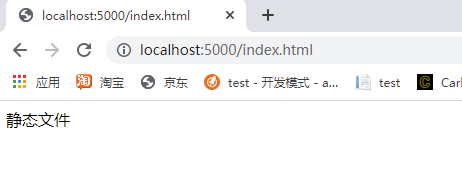
在wwwroot下建立一个index.html,那么访问http://localhost/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> </head> <body> 静态文件 </body> </html>
效果:
如果还有一些其他目录需要注册的话,那么可以这样:
app.UseStaticFiles(new StaticFileOptions
{
RequestPath="/files",
FileProvider = new PhysicalFileProvider(Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(),"files"))
});在根目录建立files:

然后呢,访问就是http://localhost:5000/files/index.html
接下来介绍一下UseDefaultFiles,这个是设置默认的文件。
这个不是说404,然后跳转到这个文件这里哈。
直接看下它的中间件间吧。
DefaultFilesMiddleware:
public Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
if (context.GetEndpoint() == null &&
Helpers.IsGetOrHeadMethod(context.Request.Method)
&& Helpers.TryMatchPath(context, _matchUrl, forDirectory: true, subpath: out var subpath))
{
var dirContents = _fileProvider.GetDirectoryContents(subpath.Value);
if (dirContents.Exists)
{
// Check if any of our default files exist.
for (int matchIndex = 0; matchIndex < _options.DefaultFileNames.Count; matchIndex++)
{
string defaultFile = _options.DefaultFileNames[matchIndex];
var file = _fileProvider.GetFileInfo(subpath.Value + defaultFile);
// TryMatchPath will make sure subpath always ends with a "/" by adding it if needed.
if (file.Exists)
{
// If the path matches a directory but does not end in a slash, redirect to add the slash.
// This prevents relative links from breaking.
if (!Helpers.PathEndsInSlash(context.Request.Path))
{
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status301MovedPermanently;
var request = context.Request;
var redirect = UriHelper.BuildAbsolute(request.Scheme, request.Host, request.PathBase, request.Path + "/", request.QueryString);
context.Response.Headers[HeaderNames.Location] = redirect;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// Match found, re-write the url. A later middleware will actually serve the file.
context.Request.Path = new PathString(context.Request.Path.Value + defaultFile);
break;
}
}
}
}
return _next(context);
}里面做的事情其实很简单,将请求转换为文件路径。分为末尾是/和末尾不是/的。
比如http://localhost/a/,那么转换为wwwroot/a/路径。然后判断context.Request.Path末尾是否是/,如果是那么给文件路径加上index.html或者其他默认文件。如果判断存在的话,那么返回文件。
比如http://localhost/a,那么转换为wwwroot/a/路径。然后判断context.Request.Path末尾是不是/,如果是那么给文件路径加上index.html或者其他默认文件。如果判断存在的话,那么给路径加上/,然后返回301重新请求。
默认的在DefaultFilesOptions:
/// <summary>
/// Options for selecting default file names.
/// </summary>
public class DefaultFilesOptions : SharedOptionsBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Configuration for the DefaultFilesMiddleware.
/// </summary>
public DefaultFilesOptions()
: this(new SharedOptions())
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Configuration for the DefaultFilesMiddleware.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sharedOptions"></param>
public DefaultFilesOptions(SharedOptions sharedOptions)
: base(sharedOptions)
{
// Prioritized list
DefaultFileNames = new List<string>
{
"default.htm",
"default.html",
"index.htm",
"index.html",
};
}
/// <summary>
/// An ordered list of file names to select by default. List length and ordering may affect performance.
/// </summary>
public IList<string> DefaultFileNames { get; set; }
}有上面这几个默认的,以此按照顺序,当然你也可以传进去修改,看下参数就好。
a目录建立了一个index.html:
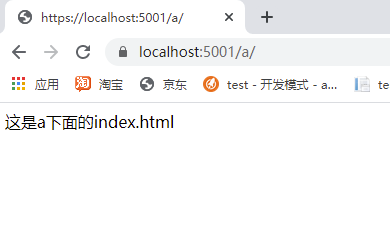
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> </head> <body> 这是a下面的index.html </body> </html>
那么访问http://localhost:5000/a 就好。
效果:
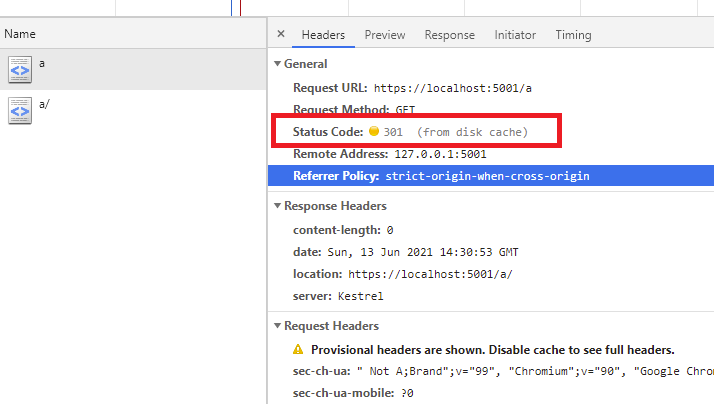
经过了一次301哈。
那么介绍一下目录预览:
增加服务:
services.AddDirectoryBrowser();
增加中间件:
app.UseDirectoryBrowser();
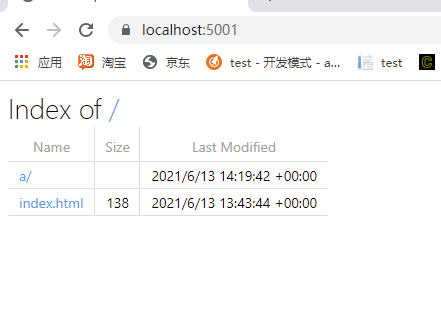
这样就可以了。
如果我们前后端像这种不完全分离的情况有一个问题。
比如说,现在一般3大框架,vue和 angular,react这种的话。你会发现一个问题,那就是他们有自己的路由。
这个时候可能就会和我们的路由冲突。
比如说http://localhost/pay 需要访问的是index.html。因为index.html有自己的路由,显示pay页面。
那么配置路由的时候应该加一条。
app.MapWhen(context =>
{
return !context.Request.Path.Value.StartsWith("/api");
}, builder =>
{
var option = new RewriteOptions();
option.AddRewrite(".*","/index.html",true);
app.UseRewriter(option);
app.UseStaticFiles();
});就是如果不是/api开头的,统一定位到index.html,然后再经过UseStaticFiles处理,就直接到了index.html。
RewriteOptions这些转换在细节篇中介绍。当然你也可以直接去给HttpContext body注入index.html流,然后返回,但是这样用不到一些其他特性,就不介绍了。
到此,相信大家对“.net core静态中间件有什么作用”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。