小编给大家分享一下Android如何利用Sensor实现传感器功能,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后都有所收获,下面让我们一起去探讨吧!
具体内容如下
1、传感器的类型:
方向传感器::Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION
加速度(重力)传感器:sensor.TYPE_ACCELEFOMETER
光线传感器:sensor.TYPT_LIGHT
磁场传感器:sensor.TYPE_MANGNETIC_FIELD
距离(临近性)传感器:Sensor.TYPE_FROXIMITY
温度传感器:Sensor.TYPE_TEMPERATURE
常用的API:
<1>得到传感器的服务(得到传感器的管理者)
SensorManager sm=(SensorManager)getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
<2>得到手机所支持的所有的传感器的类型:
List list=sm.getSensorList(SensorManager.TYPE_ALL);
<3>传感器的类型:
Sensor.getType();
<4>传感器的名字;
Sensor.getName();
<5>传感器的监听:SensorEventListener()
sm.registerListener(监听,传感器对象,rate);
重点:
<1>光线传感器:sensor.TYPT_LIGHT
得到光线值:float f=event.values[0];
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = activity.getWindow().getAttributes();
params.screenBrightness = value / 255f;
activity.getWindow().setAttributes(params);
<2>加速度传感器:sensor.TYPE_ACCELEFOMETER
加速度有三个值:这三个值是手机在三个方向受到的加速度
float x=event.values[0];–>在手机顶部从左边沿往有边沿是手机的X轴的正方向
float y=event.values[1];–>从手机顶部沿手机左边沿手机底部是Y轴的正方向
float z=event.values[2];–>垂直手机屏幕朝外的是正方向
<3>方向传感器:Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION
方向传感器三个值:
方向角:指手机平躺时,手机头部绕Z轴旋转,与地球正北极的夹角
0代表北(North)
90代表东East
180代表南(South)
270代表西(West)
俯视角:手机绕X轴旋转与水平线的夹角
滚转角:手机绕Y轴旋转与水平线的夹角
利用方向传感器实现 指南针应用
运行后效果图如下:
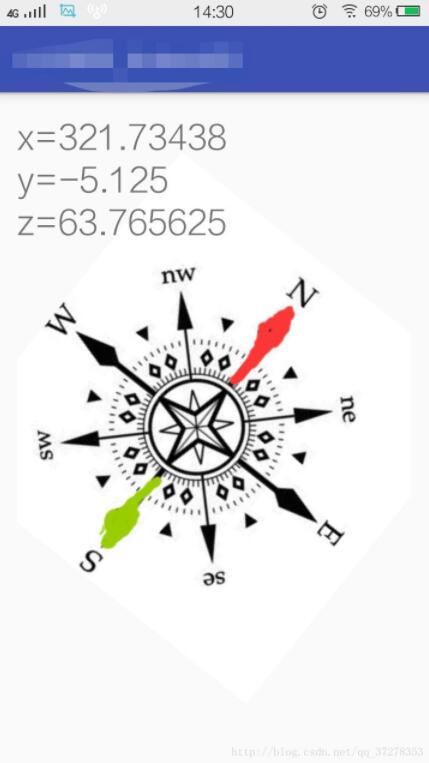
布局文件(activity_main.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/activity_main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.example.g150825_android29.MainActivity"> <ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/znz" android:id="@+id/iv_image" />I <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="30sp" android:id="@+id/tv_main_result" /> </RelativeLayout>
Java代码(MainActivity )
package com.example.g150825_android29;
import android.content.Context;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.RotateAnimation;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private SensorManager sensorManager;
private Sensor sensorOri;
private TextView tv_main_result;
private MyListener myListener;
private ImageView iv_image;
private float current=0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_main_result = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_main_result);
iv_image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_image);
//得到传感器管理者
sensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE);
//得到光线传感器
// sensorLight = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_LIGHT);
//获取加速度传感器
// sensorACC = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
//获取方向传感器
sensorOri=sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION);
//获取光线传感器的值(光线值)
myListener = new MyListener();
}
//注册监听(监听某一个传感器的值)
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
sensorManager.registerListener(myListener,sensorOri,SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
}
class MyListener implements SensorEventListener{
//当值发生改变
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent sensorEvent) {
float[] f=sensorEvent.values;
float x=f[0];
float y=f[1];
float z=f[2];
tv_main_result.setText("x="+x+"\ny="+y+"\nz="+z);
//实例化旋转动画
RotateAnimation rotateAnimation=new RotateAnimation(current,-x, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f);
rotateAnimation.setDuration(200);
current=-x;
iv_image.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);
//改变屏幕的亮度
// WindowManager.LayoutParams layoutParams=getWindow().getAttributes();
// layoutParams.screenBrightness=light/255f;
// getWindow().setAttributes(layoutParams);
}
//当值的精度发生改变
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int i) {
}
}
//取消注册监听
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
sensorManager.unregisterListener(myListener);
}
// public void getAllSensors(View view){
// List<Sensor> sensors=sensorManager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ALL);
// for(Sensor s:sensors){
// Log.i("test", s.getName());
// }
//
// }
}看完了这篇文章,相信你对“Android如何利用Sensor实现传感器功能”有了一定的了解,如果想了解更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。