这篇文章主要为大家展示了“pytorch中的torch.nn.Conv2d()函数怎么用”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“pytorch中的torch.nn.Conv2d()函数怎么用”这篇文章吧。
官网
nn.Conv2d:对由多个输入平面组成的输入信号进行二维卷积


参数详解
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
| 参数 | 参数类型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| in_channels | int | Number of channels in the input image | 输入图像通道数 |
| out_channels | int | Number of channels produced by the convolution | 卷积产生的通道数 |
| kernel_size | (int or tuple) | Size of the convolving kernel | 卷积核尺寸,可以设为1个int型数或者一个(int, int)型的元组。例如(2,3)是高2宽3卷积核 |
| stride | (int or tuple, optional) | Stride of the convolution. Default: 1 | 卷积步长,默认为1。可以设为1个int型数或者一个(int, int)型的元组。 |
| padding | (int or tuple, optional) | Zero-padding added to both sides of the input. Default: 0 | 填充操作,控制padding_mode的数目。 |
| padding_mode | (string, optional) | ‘zeros’, ‘reflect’, ‘replicate’ or ‘circular’. Default: ‘zeros’ | padding模式,默认为Zero-padding 。 |
| dilation | (int or tuple, optional) | Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1 | 扩张操作:控制kernel点(卷积核点)的间距,默认值:1。 |
| groups | (int, optional) | Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1 | group参数的作用是控制分组卷积,默认不分组,为1组。 |
| bias | (bool, optional) | If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True | 为真,则在输出中添加一个可学习的偏差。默认:True。 |
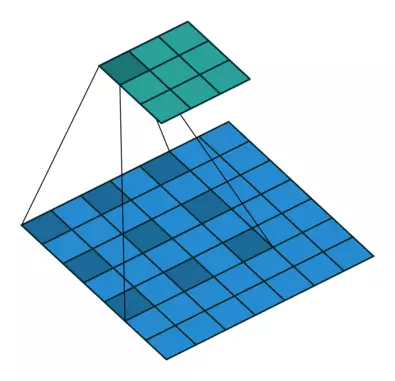
dilation操作动图演示如下:
Dilated Convolution with a 3 x 3 kernel and dilation rate 2
扩张卷积核为3×3,扩张率为2
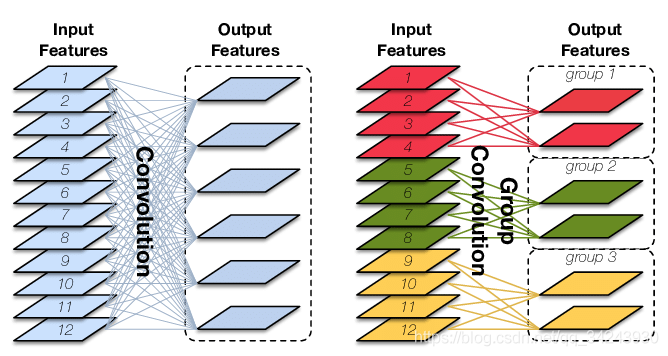
Group Convolution顾名思义,则是对输入feature map进行分组,然后每组分别卷积。

三、代码实例
import torch x = torch.randn(3,1,5,4) print(x) conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(1,4,(2,3)) res = conv(x) print(res.shape) # torch.Size([3, 4, 4, 2])
输入:x[ batch_size, channels, height_1, width_1 ]
batch_size,一个batch中样本的个数 3
channels,通道数,也就是当前层的深度 1
height_1, 图片的高 5
width_1, 图片的宽 4
卷积操作:Conv2d[ channels, output, height_2, width_2 ]
channels,通道数,和上面保持一致,也就是当前层的深度 1
output ,输出的深度 4【需要4个filter】
height_2,卷积核的高 2
width_2,卷积核的宽 3
输出:res[ batch_size,output, height_3, width_3 ]
batch_size,,一个batch中样例的个数,同上 3
output, 输出的深度 4
height_3, 卷积结果的高度 4
width_3,卷积结果的宽度 2
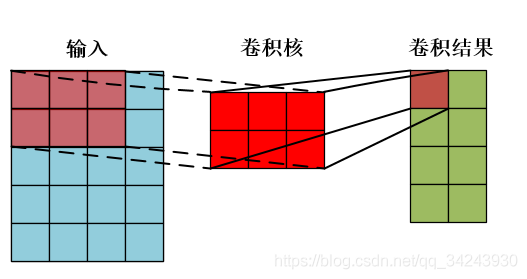
一个样本卷积示例:
以上是“pytorch中的torch.nn.Conv2d()函数怎么用”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。