本篇内容介绍了“基于Matlab怎么实现野狗优化算法”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!

野狗优化算法(Dingo Optimization Algorithm, DOA)模仿澳大利亚野狗的社交行为。DOA算法的灵感来源于野狗的狩猎策略,即迫害攻击、分组策略和食腐行为。为了提高该方法的整体效率和性能,在DOA中制定了三种与四条规则相关联的搜索策略,这些策略和规则在搜索空间的强化(开发)和多样化(探索)之间提供了一种精确的平衡。
该算法的优点:寻优能力强,收敛速度快等特点。

野狗种群在搜索边界内随机初始化:
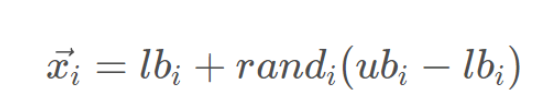
其中,lbi和ubi分别表示个体的上下边界,randi是[0,1]之间的随机数。
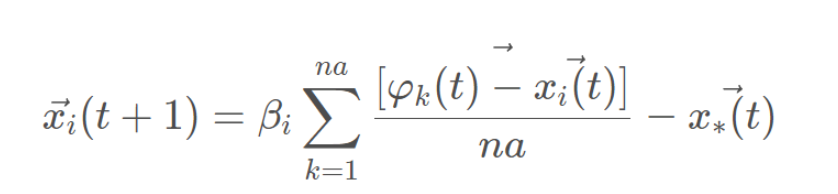
捕食者通常使用高度智能的狩猎技术,野狗通常单独捕食小猎物,如兔子,但当捕食大猎物,如袋鼠时,它们会成群结队。野狗能找到猎物的位置并将其包围,其行为如上所示:
其中,t代表当前的迭代次数,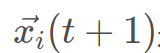 是野狗新位置; na是在[2,SizePop/2]的逆序中生成的随机整数,其中SizePop是野狗种群的规模;
是野狗新位置; na是在[2,SizePop/2]的逆序中生成的随机整数,其中SizePop是野狗种群的规模; 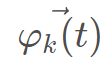 是将攻击的野狗的子集,其中
是将攻击的野狗的子集,其中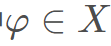 是随机生成的野狗种群;
是随机生成的野狗种群;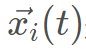 是当前野狗的位置
是当前野狗的位置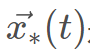 是上一次迭代中发现的最佳野狗;β1是在[-2.2]内均匀生成的随机数,它是一个比例因子,可改变野狗轨迹的大小。
是上一次迭代中发现的最佳野狗;β1是在[-2.2]内均匀生成的随机数,它是一个比例因子,可改变野狗轨迹的大小。
野狗通常捕猎小猎物,直到单独捕获为止。行为模拟为:
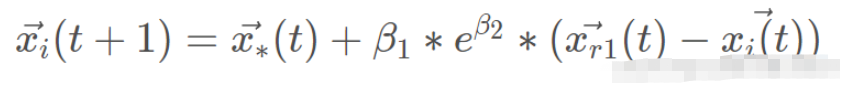
其中,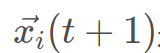 是野狗新位置,
是野狗新位置,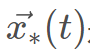 是上一次迭代中发现的最佳野狗,β2的值与式2.2中的值相同,β2是在[-1,1]区间内均匀生成的随机数,r1是在从1到最大搜索代理(野狗)大小的区间内生成的随机数,
是上一次迭代中发现的最佳野狗,β2的值与式2.2中的值相同,β2是在[-1,1]区间内均匀生成的随机数,r1是在从1到最大搜索代理(野狗)大小的区间内生成的随机数,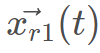 是随机选择的第r1个野狗,其中i≠r1。
是随机选择的第r1个野狗,其中i≠r1。
在DOA中,野狗的存活率值由下式给出:
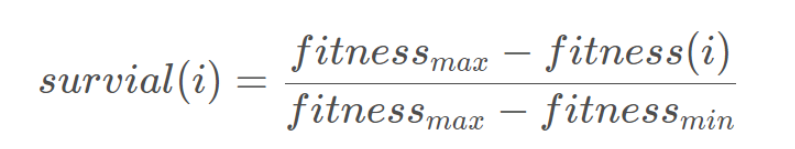
其中,fitnessmax和fitnessmin分别是当前一代中最差和最佳的适应度值,而fitness(i)是第i个野狗的当前适应度值。式(5)中的生存向量包含[0,1]区间内的归一化适应度。
%====欢迎关注公众号:电力系统与算法之美====
function DOA()
%% ====参数设置====
popsize=20; % 种群规模
Iteration=1000; % 迭代次数
lb = -10; % 各维度的下限
ub = 10; % 各维度的上限
dim = 2; % 优化变量的个数
P= 0.5; % Hunting or Scavenger rate.
Q= 0.7; % Group attack or persecution?
beta1= -2 + 4* rand(); % -2 < beta < 2
beta2= -1 + 2* rand(); % -1 < beta2 < 1
naIni= 2; % minimum number of dingoes that will attack
naEnd= popsize /naIni; % maximum number of dingoes that will attack
na= round(naIni + (naEnd-naIni) * rand()); % number of dingoes that will attack
%% ====初始化种群位置=====
Positions=lb + (ub - lb).*rand(popsize, dim);
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
Fitness(i)=sum(Positions(i,:).^2); % get fitness
end
[best_score, minIdx]= min(Fitness); % the min fitness value vMin and the position minIdx
best_x= Positions(minIdx,:); % the best vector
[worst_score, ~]= max(Fitness); % the max fitness value vMax and the position maxIdx
curve=zeros(1,Iteration);
%% Section 2.2.4 Dingoes'survival rates
for i=1:size(Fitness,2)
survival(i)= (worst_score-Fitness(i))/(worst_score - best_score);
end
%% =====开始循环===========
for t=1:Iteration
for r=1:popsize
if rand() < P % Hunting
sumatory=0;
c=1;
vAttack=[];
while(c<=na)
idx =round( 1+ (popsize-1) * rand());
band= 0;
for i=1:size(vAttack, 2)
if idx== vAttack(i)
band=1;
break;
end
end
if ~band
vAttack(c) = idx;
c=c+1;
end
end
for j=1:size(vAttack,2)
sumatory= sumatory + Positions(vAttack(j),:)- Positions(r,:);
end
sumatory=sumatory/na;
if rand() < Q % group attack
v(r,:)= beta1 * sumatory-best_x; % Strategy 1: Eq.2
else % Persecution
r1= round(1+ (popsize-1)* rand()); %
v(r,:)= best_x + beta1*(exp(beta2))*((Positions(r1,:)-Positions(r,:))); %
end
else % Scavenger
r1= round(1+ (popsize-1)* rand());
if rand() < 0.5
val= 0;
else
val=1;
end
v(r,:)= (exp(beta2)* Positions(r1,:)-((-1)^val)*Positions(r,:))/2; %
end
if survival(r) <= 0.3 % Section 2.2.4, Algorithm 3 - Survival procedure
band=1;
while band
r1= round(1+ (popsize-1)* rand());
r2= round(1+ (popsize-1)* rand());
if r1 ~= r2
band=0;
end
end
if rand() < 0.5
val= 0;
else
val=1;
end
v(r,:)= best_x + (Positions(r1,:)-((-1)^val)*Positions(r2,:))/2; % Section 2.2.4, Strategy 4: Eq.6
end
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space .
Flag4ub=v(r,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=v(r,:)<lb;
v(r,:)=(v(r,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Evaluate new solutions
Fnew= sum(v(r,:).^2);
% Update if the solution improves
if Fnew <= Fitness(r)
Positions(r,:)= v(r,:);
Fitness(r)= Fnew;
end
if Fnew <= best_score
best_x= v(r,:);
best_score= Fnew;
end
end
curve(t)= best_score;
[worst_score, ~]= max(Fitness);
for i=1:size(Fitness,2)
survival(i)= (worst_score-Fitness(i))/(worst_score - best_score);
end
end
%======结束优化===============
%% 进化曲线
figure
semilogy(curve,'Color','r','LineWidth',2)
grid on
title('收敛曲线')
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('最佳适应度');
axis tight
legend('DOA')
display(['最优解: ', num2str(best_x)]);
display(['最小值: ', num2str(best_score)]);
end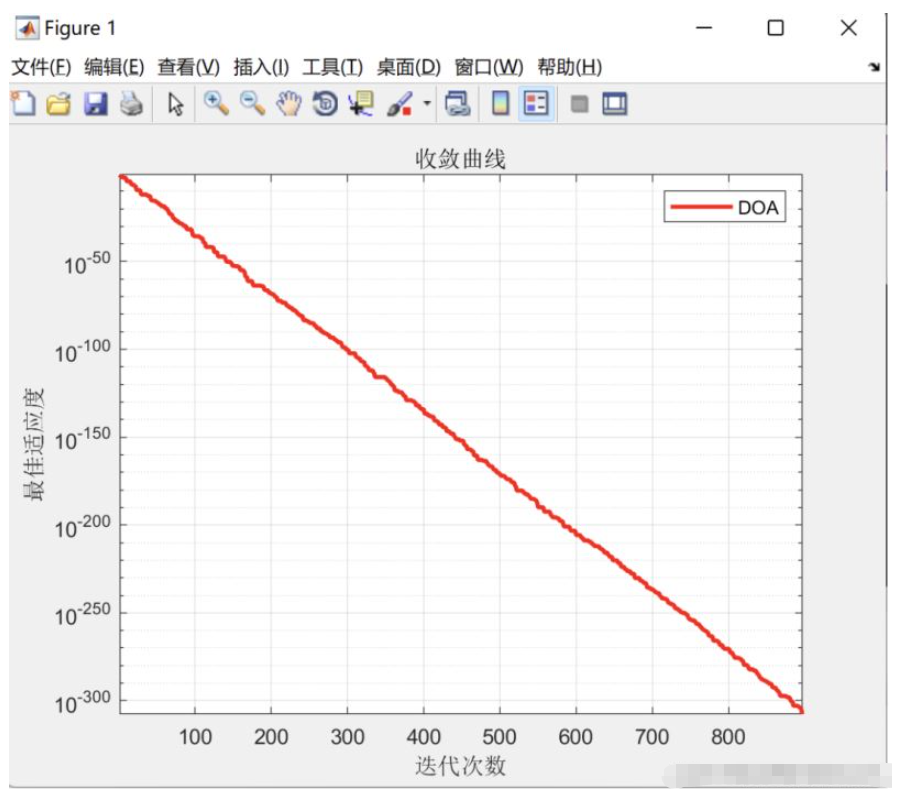
“基于Matlab怎么实现野狗优化算法”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。