这篇文章主要介绍了如何使用Go语言写一个Http Server的相关知识,内容详细易懂,操作简单快捷,具有一定借鉴价值,相信大家阅读完这篇如何使用Go语言写一个Http Server文章都会有所收获,下面我们一起来看看吧。
Http Server 代码
go.mod:
module goStudy1 go 1.17
main.go:
package main import ( "fmt" "os" "strconv" //"github.com/thinkeridea/go-extend/exnet" "io" "log" "net/http" "strings" ) /* 编写一个 HTTP 服务器,4个功能: 1,接收客户端 request,并将 request 中带的 header 写入 response header 2,读取当前系统的环境变量中的 VERSION 配置,并写入 response header 3,Server 端记录访问日志包括客户端 IP,HTTP 返回码,输出到 server 端的标准输出 4,当访问 localhost/healthz 时,应返回 200 */ // Main方法入口 func main() { println("环境正常") // 功能1 http.HandleFunc("/requestAndResponse", requestAndResponse) // 功能2 http.HandleFunc("/getVersion", getVersion) // 功能3 http.HandleFunc("/ipAndStatus", ipAndStatus) //注册接口句柄 // 功能4 http.HandleFunc("/healthz", healthz) //注册接口句柄 err := http.ListenAndServe(":81", nil) //监听空句柄,80端口被占用,使用81端口 if nil != err { log.Fatal(err) //显示错误日志 } } // 功能1,接收请求及响应 func requestAndResponse(response http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) { println("调用requestAndResponse接口") headers := request.Header //header是Map类型的数据 println("传入的hander:") for header := range headers { //value是[]string //println("header的key:" + header) values := headers[header] for index, _ := range values { values[index] = strings.TrimSpace(values[index]) //println("index=" + strconv.Itoa(index)) //println("header的value:" + values[index]) } //valueString := strings.Join(values, "") //println("header的value:" + valueString) println(header + "=" + strings.Join(values, ",")) //打印request的header的k=v response.Header().Set(header, strings.Join(values, ",")) // 遍历写入response的Header //println() } fmt.Fprintln(response, "Header全部数据:", headers) io.WriteString(response, "succeed") } // 功能2,获取环境变量的version func getVersion(response http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) { println("调用getVersion接口") envStr := os.Getenv("VERSION") //envStr := os.Getenv("HADOOP_HOME") //println("系统环境变量:" + envStr) //可以看到 C:\soft\hadoop-3.3.1 Win10需要重启电脑才能生效 response.Header().Set("VERSION", envStr) io.WriteString(response, "succeed") } // 功能3,输出IP与返回码 func ipAndStatus(response http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) { println("调用ipAndStatus接口") form := request.RemoteAddr println("Client->ip:port=" + form) //虚拟机是桥接模式。使用postman返回的全部是127.0.0.1 用手机打开网站192.168.1.139:81/ipAndStatus可以看到新IP ipStr := strings.Split(form, ":") println("Client->ip=" + ipStr[0]) //打印ip // 获取http响应码 //response.WriteHeader(301) //手动设置响应码,默认200 //response.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)//由于默认是调用这个,∴返回码都是这个200【server.go有源码】 println("Client->response code=" + strconv.Itoa(http.StatusOK)) //println("response code->:" + code) io.WriteString(response, "succeed") } // 功能4,连通性测试接口 func healthz(response http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) { println("调用healthz接口") response.WriteHeader(200) //设置返回码200 //response.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)//默认会调用这个方法,默认就是200【server.go有源码】 io.WriteString(response, "succeed") }
由于80端口被占用,使用了81端口。
由于Linux虚拟机没有安装go环境,只有windows有go环境,使用goland开发后,用postman调试。
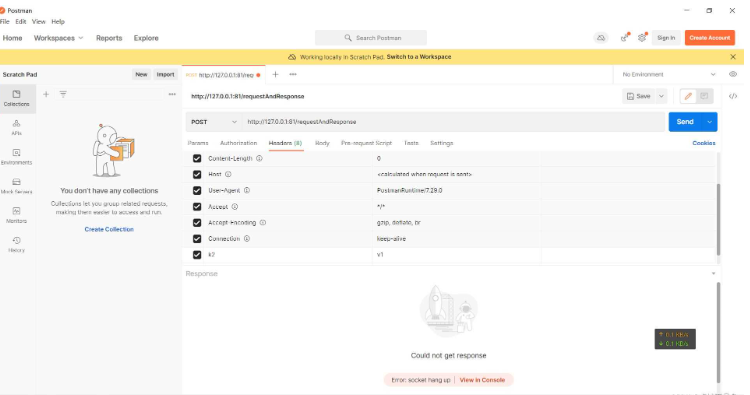
POST的request中额外配置了 k2=v1 。Send后可以看到:
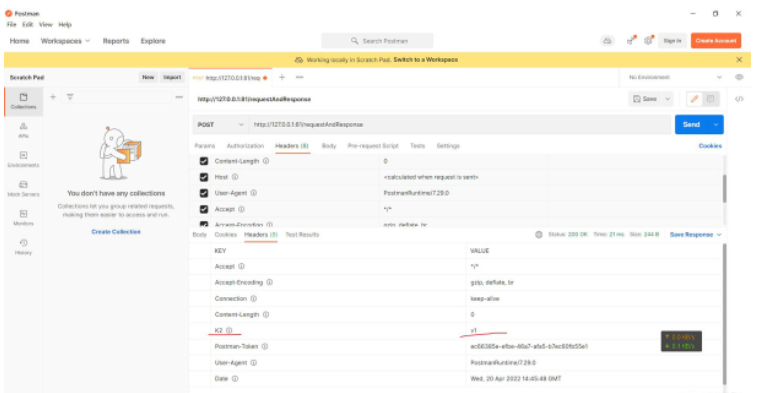
Response中出现了手动新增的请求头及其它默认的请求头。【原始的response只有3对kv结果,已经遍历添加成功】。说明成功写入。
由于Windows需要重启才能刷新环境变量,故:
//envStr := os.Getenv("VERSION")
envStr := os.Getenv("HADOOP_HOME")测试时,此处读取已经存在的环境变量,原理是一致的。
网站:http://127.0.0.1:81/getVersion
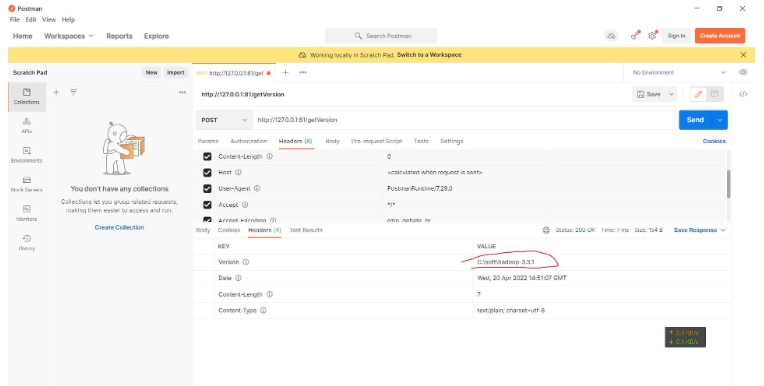
说明Go可以读取到环境变量的值,并且写入response的headers。
网站:http://127.0.0.1:81/ipAndStatus
分别用postman、手机请求这个网站【手机请求时需要和PC在同一个路由,将网站IP更换为PC的IP才可以访问】,goland中显示:
环境正常 调用getVersion接口 调用ipAndStatus接口 Client->ip:port=127.0.0.1:59595 Client->ip=127.0.0.1 Client->response code=200 调用ipAndStatus接口 Client->ip:port=192.168.1.138:37548 Client->ip=192.168.1.138 Client->response code=200
显然读取到了client的IP。由于server.go中有写:
// WriteHeader sends an HTTP response header with the provided // status code. // // If WriteHeader is not called explicitly, the first call to Write // will trigger an implicit WriteHeader(http.StatusOK). // Thus explicit calls to WriteHeader are mainly used to // send error codes. // // The provided code must be a valid HTTP 1xx-5xx status code. // Only one header may be written. Go does not currently // support sending user-defined 1xx informational headers, // with the exception of 100-continue response header that the // Server sends automatically when the Request.Body is read. WriteHeader(statusCode int)
默认的响应头就是取返回值为200,不设置就是按照默认的200来返回,故此处的响应码为200。
由于响应体引用的请求体并不包含返回码,如果直接从响应体的请求中拿返回码【request.Response.StatusCode】,会报内存错误及空指针的panic。
网址:http://127.0.0.1:81/healthz
使用postman调用接口,可以看到:
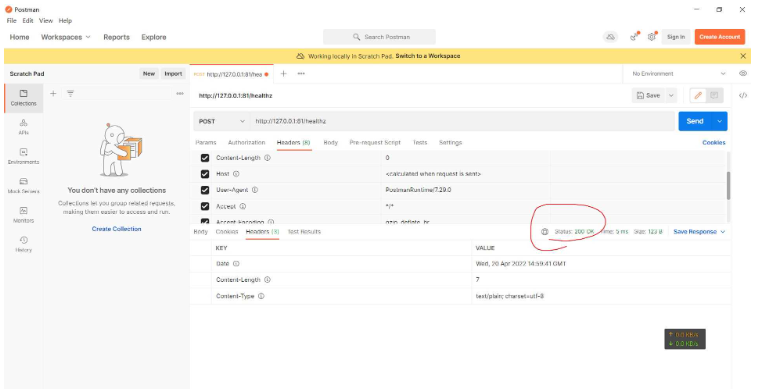
默认的响应体的响应头的返回码就是200。且返回值3个。
可以看出,Go相比Java还是很简洁的。
关于“如何使用Go语言写一个Http Server”这篇文章的内容就介绍到这里,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家对“如何使用Go语言写一个Http Server”知识都有一定的了解,大家如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。