本篇内容主要讲解“Android如何实现简单实用的垂直进度条”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Android如何实现简单实用的垂直进度条”吧!
支持属性:
progress_radius 进度条圆角大小
progress_border_enable 进度条是否有边框
progress_gradient_enable 进度条颜色是否渐变
progress_start_color 从上到下进度条开始的渐变色
progress_end_color 从上到下进度条结束的渐变色
progress_solid_color 带边框进度条的背景填充色
progress_border_color 进度条边框的颜色
progress_border_width 进度条边框的宽度
有需要定义其他属性的,可以进行扩充下面是效果图
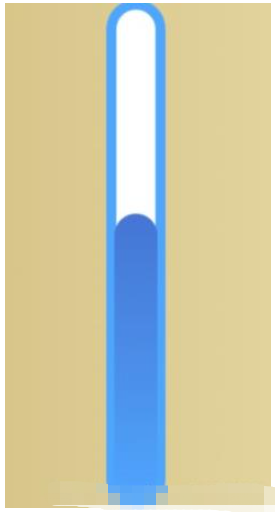
上代码
VerticalProgress
public class VerticalProgress extends View {
//进度条圆角
private int mRadius;
//进度条是否有边框
private boolean mBorderEnable;
//是否有渐变色
private boolean mGradientEnable;
//渐变色
private int mStartResId;
private int mEndResId;
//边框的颜色
private int mBorderColorResId;
//进度条背景填充色
private int mProgressBgColorId;
//边框宽度
private int mBorderWidth;
private int mProgress = 10;
private int max = 100;
private int mWidth;
private int mHeight;
private RectF mRectF;
private Paint mPaint;
public VerticalProgress(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context, null);
}
public VerticalProgress(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mWidth = getMeasuredWidth() - 1;// 宽度值
mHeight = getMeasuredHeight() - 1;// 高度值
}
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray typedArray = null;
if (attrs != null) {
typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.verticalProgress);
mRadius = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_radius, 0);
mBorderEnable = typedArray.getBoolean(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_border_enable, false);
mGradientEnable = typedArray.getBoolean(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_gradient_enable, true);
mStartResId = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_start_color, R.color.colorPrimary);
mProgressBgColorId = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_solid_color, R.color.white);
mEndResId = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_end_color, R.color.color_4EA6FD);
mBorderColorResId = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_border_color, R.color.color_4EA6FD);
mBorderWidth = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.verticalProgress_progress_border_width, 10);
}
if (typedArray != null) {
typedArray.recycle();
}
mRectF = new RectF();
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
}
@SuppressLint("DrawAllocation")
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (mRadius == 0) {
//弧度为高度的一半
mRadius = mWidth / 2;
}
if (mBorderEnable) {
//第一层矩形(描边层)
mRectF.set(0, 0, mWidth, mHeight);
//第一层矩形颜色(进度条描边的颜色)
mPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(mBorderColorResId));
//画第一层圆角矩形
canvas.drawRoundRect(mRectF, mRadius, mRadius, mPaint);
//第二层矩形颜色(背景层颜色)
mPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(mProgressBgColorId));
//第二层矩形(背景层)
mRectF.set(mBorderWidth, mBorderWidth, mWidth - mBorderWidth, mHeight - mBorderWidth);
//画背景层圆角矩形(盖在描边层之上)
canvas.drawRoundRect(mRectF, mRadius, mRadius, mPaint);
}
if (mProgress == 0)//进度为 0不画进度
return;
float section = mProgress / max;
//进度层底层
mRectF.set(+8, mHeight - mProgress / 100f * mHeight + 10, mWidth - 8, mHeight - 8);
if (mGradientEnable) {
//渐变器
LinearGradient shader = new LinearGradient(0, 0, mWidth * section, mHeight,
getResources().getColor(mStartResId), getResources().getColor(mEndResId), Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
//第三层矩形颜色(进度渐变色)
mPaint.setShader(shader);
}
//画第三层(进度层)圆角矩形(盖在背景层之上)
canvas.drawRoundRect(mRectF, mRadius, mRadius, mPaint);
//清除之前传递的shader
mPaint.setShader(null);
}
public void setProgress(int currentCount) {
this.mProgress = currentCount > max ? max : currentCount;
postInvalidate();
}
}attr.xml样式
<declare-styleable name="verticalProgress">
<attr name="progress_radius" format="dimension" />
<attr name="progress_border_width" format="dimension" />
<attr name="progress_gradient_enable" format="boolean" />
<attr name="progress_border_enable" format="boolean" />
<attr name="progress_start_color" format="color" />
<attr name="progress_solid_color" format="color" />
<attr name="progress_end_color" format="color" />
<attr name="progress_border_color" format="boolean" />
</declare-styleable>最后调用示例
<com.widget.VerticalProgress
android:id="@+id/vp_progress"
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:progress_border_enable="true"
app:progress_solid_color="@color/white"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />到此,相信大家对“Android如何实现简单实用的垂直进度条”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。