这篇文章主要讲解了“Spring自动注入的应用”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Spring自动注入的应用”吧!
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
// class com.ypf.ServiceB
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
// 关键点 !!! 去 spring ioc 容器中找到需要注入的 type 类型的 bean
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
// Determine the autowire candidate in the given set of beans.
// Looks for {@code @Primary} and {@code @Priority} (in that order).
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(type, matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
// 将得到的 bean 从 matchingBeans 这个 map 中取出来。
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
// 为什么要加入 成功注入 beanName 放到一个 Set 集合中
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
// ???
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}依赖描述器,大概描述了 XXX 里的 field 需要自动装配 xxx 类型的 bean。
descriptor.resolveCandidate 里面实际上就是调用了 getBean
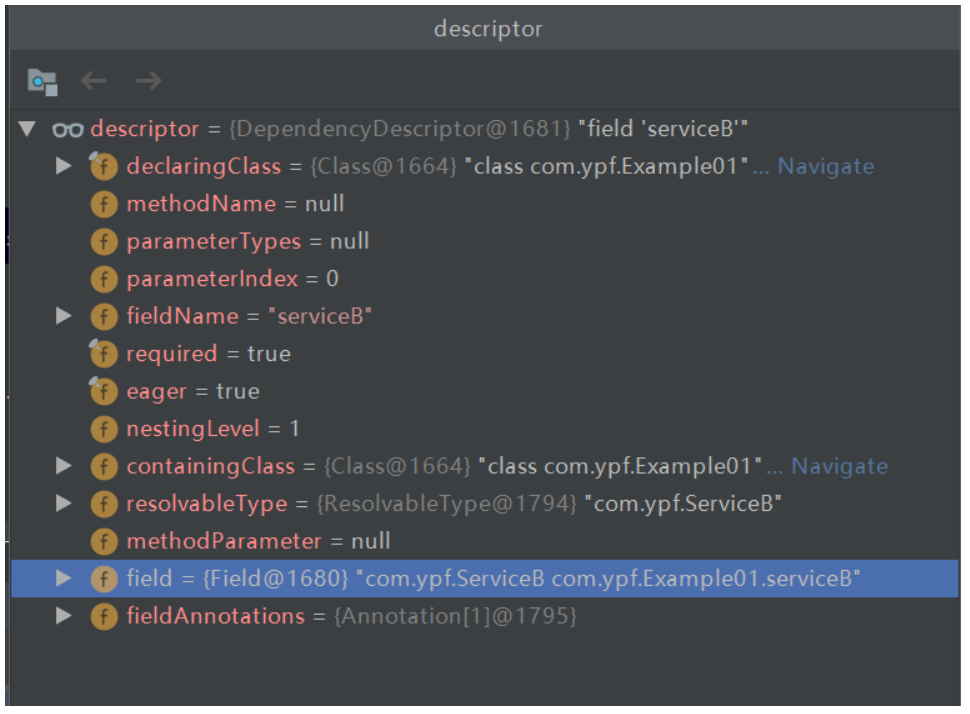
根据一些规则找到一些 candidateNames,把这些 candidateName,beanInstance 放到 map 中返回。 beanInstance 是根据调用 getBean(candidateName) 得到的。
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(
@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
// 先根据自动装配的 Class 类型去找到 spring ioc 容器中的所有是这种类型的 bean 的 name。
// Ancestors 祖先
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(candidateNames.length);
// 解析过的依赖会被缓存起来,根据 requiredType 去看缓存中没有有,有的话直接取出来
for (Class<?> autowiringType : this.resolvableDependencies.keySet()) {
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = this.resolvableDependencies.get(autowiringType);
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
// 如果自动装配的属性的类型不是这个类,且是自动装配的候选就加入到 result。按 byType
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty() && !indicatesMultipleBeans(requiredType)) {
// Consider fallback matches if the first pass failed to find anything...
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
// 如果自动装配的属性的类型不是这个类,且是自动装配的候选就加入到 result。按 byName 去找。
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
// Consider self references as a final pass...
// but in the case of a dependency collection, not the very same bean itself.
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) &&
(!(descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) || !beanName.equals(candidate)) &&
isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}???
先按 byType 去找,然后去按 byName 去找?
protected boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor, AutowireCandidateResolver resolver)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
String beanDefinitionName = BeanFactoryUtils.transformedBeanName(beanName);
if (containsBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName)) {
return isAutowireCandidate(beanName, getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName), descriptor, resolver);
}
else if (containsSingleton(beanName)) {
return isAutowireCandidate(beanName, new RootBeanDefinition(getType(beanName)), descriptor, resolver);
}
BeanFactory parent = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
// No bean definition found in this factory -> delegate to parent.
return ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) parent).isAutowireCandidate(beanName, descriptor, resolver);
}
else if (parent instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
// If no DefaultListableBeanFactory, can't pass the resolver along.
return ((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) parent).isAutowireCandidate(beanName, descriptor);
}
else {
return true;
}
}感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Spring自动注入的应用”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Spring自动注入的应用这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4196131/blog/3100067