本篇内容介绍了“Java Spring的两种事务是什么”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
Spring的事务控制可以分为编程式事务控制和声明式事务控制。
编程式
开发者直接把事务的代码和业务代码耦合到一起,在实际开发中不用。
声明式
开发者采用配置的方式来实现的事务控制,业务代码与事务代码实现解耦合,使用的AOP思想。
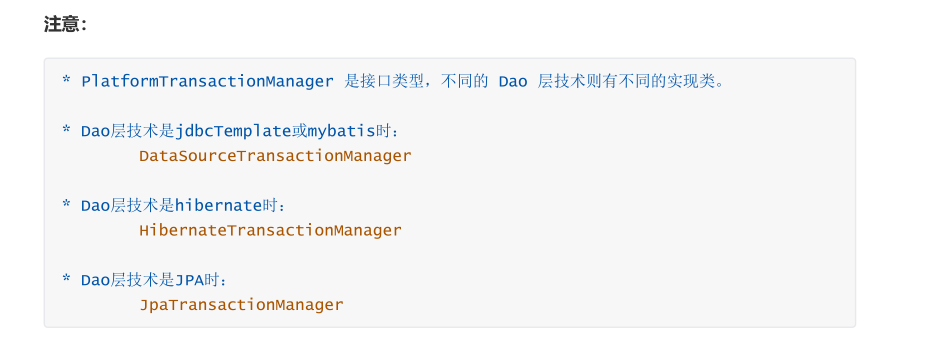
PlatformTransactionManager接口,是spring的事务管理器接口,里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法。
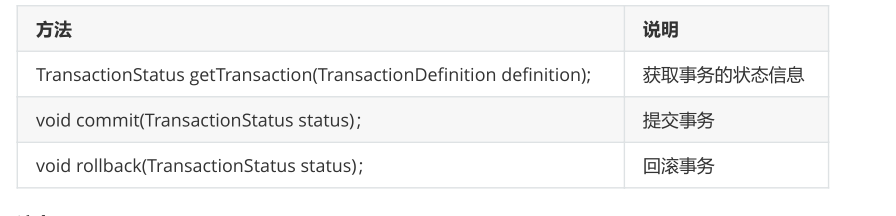
TransactionDefinition接口提供事务的定义信息(事务隔离级别、事务传播行为等等)
(1)事务隔离级别
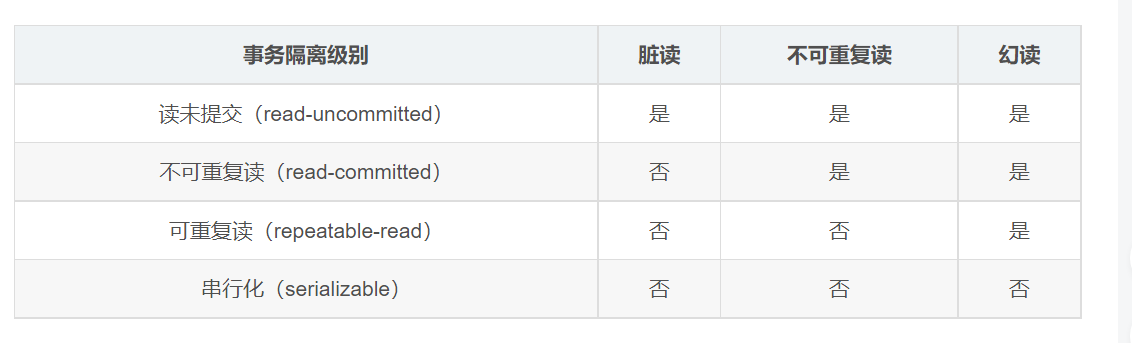
设置隔离级别,可以解决事务并发产生的问题,如脏读、不可重复读和虚读(幻读)。
注意:使用数据库默认级别,如果数据库是mysql,则默认是可重复读,oracle是读已提交。
ISOLATION_DEFAULT 使用数据库默认级别
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 读未提交
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED 读已提交(可解决脏读问题)
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ 可重复读 (可解决脏读、不可重复读)
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 串行化
可解决:
(2)事务传播行为
事务传播行为指的就是当一个业务方法【被】另一个业务方法调用时,应该如何进行事务控制。

重点:

read-only(是否只读):建议查询时设置为只读
timeout(超时时间):默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
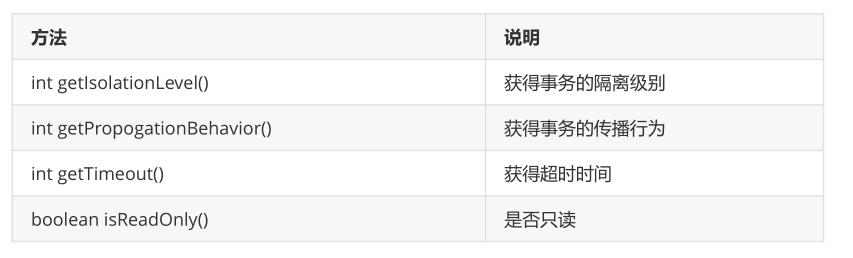
TransactionStatus 接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态。
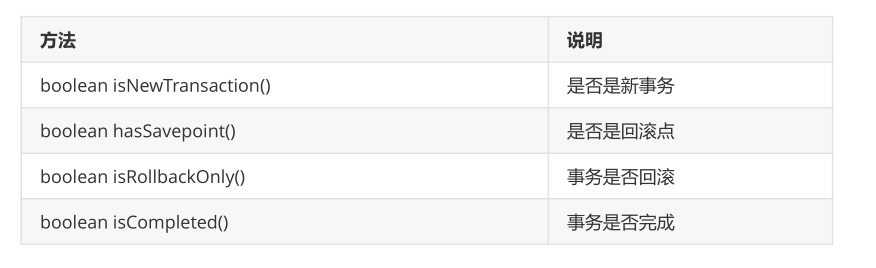
可以简单的理解三者的关系:事务管理器通过读取事务定义参数进行事务管理,然后会产生一系列的事务状态。
Spring中的事务控制主要就是通过这三个API实现的
PlatformTransactionManager 负责事务的管理,它是个接口,其子类负责具体工作
TransactionDefinition 定义了事务的一些相关参数
TransactionStatus 代表事务运行的一个实时状态
理解三者的关系:事务管理器通过读取事务定义参数进行事务管理,然后会产生一系列的事务状态。
在Spring配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。底层采用AOP思想来实现。
声明式事务控制明确事项:
核心业务代码(目标对象) (切入点是谁?)
事务增强代码(Spring已提供事务管理器))(通知是谁?)
切面配置(切面如何配置?)(切面 = 切入点 + 通知)
使用spring声明式事务控制转账业务。
步骤:
1.引入tx命名空间
2.事务管理器通知配置
3.事务管理器AOP配置
4.测试事务控制转账业务代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd ">
<!--事务管理器对象--> <!--<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>--> // 通知增强 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> //定义事务的一些属性 * 表示当前任意名称的方法都走默认配置 <!-- name: 切点方法名称 isolation:事务的隔离级别 propagation:事务的传播行为 read-only:是否只读 timeout:超时时间 --> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" timeout="-1"/> //CRUD常用配置 <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice>
当使用spring声明式管理事务,要使用aop:advisor来进行aop的配置!
//aop配置:配置切面 <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.lagou.servlet.impl.AccountServiceImpl.*(..))"/> </aop:config>-->
事务参数的配置详解:
<tx:method name=“transfer” isolation=“REPEATABLE_READ” propagation=“REQUIRED”timeout="-1" read-only=“false”/>
name:切点方法名称
isolation:事务的隔离级别
propogation:事务的传播行为
timeout:超时时间
read-only:是否只读
步骤:
修改service层,增加事务注解
修改spring核心配置文件,开启事务注解支持
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation =
Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, timeout = -1, readOnly = false)
@Override
public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
accountDao.out(outUser, money);
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(inUser, money);
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w2.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!--省略之前datsSource、jdbcTemplate、组件扫描配置--> <!--事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--事务的注解支持--> <tx:annotation-driven/> </beans
核心配置类:
@Configuration // 声明该类为核心配置类
@ComponentScan("com.lagou") // 包扫描
@Import(DataSourceConfig.class) //导入其他配置类
@EnableTransactionManagement //事务的注解驱动
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager getPlatformTransactionManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}数据源配置类:
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") //引入properties文件
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean //会把当前方法的返回值对象放进IOC容器中
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
druidDataSource.setUrl(url);
druidDataSource.setUsername(username);
druidDataSource.setPassword(password);
return druidDataSource;
}
}“Java Spring的两种事务是什么”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。