这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关MapReduce多种join实现的示例分析,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
一、概述 
对于RDBMS中的join操作大伙一定非常熟悉,写sql的时候要十分注意细节,稍有差池就会耗时巨久造成很大的性能瓶颈,而在Hadoop中使用MapReduce框架进行join的操作时同样耗时,但是由于hadoop的分布式设计理念的特殊性,因此对于这种join操作同样也具备了一定的特殊性。本文主要对MapReduce框架对表之间的join操作的几种实现方式进行详细分析,并且根据我在实际开发过程中遇到的实际例子来进行进一步的说明。
二、实现原理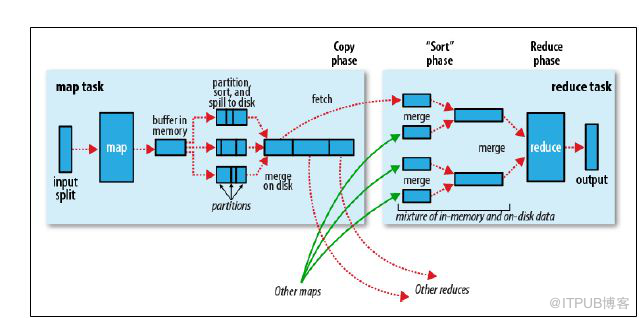
1、在Reudce端进行连接。
在Reudce端进行连接是MapReduce框架进行表之间join操作最为常见的模式,其具体的实现原理如下:
Map端的主要工作:为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
reduce端的主要工作:在reduce端以连接字段作为key的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在map阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行笛卡尔只就ok了。原理非常简单,下面来看一个实例:
(1)自定义一个value返回类型:
package com.mr.reduceSizeJoin;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class CombineValues implements WritableComparable<CombineValues>{
//private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CombineValues.class);
private Text joinKey;//链接关键字
private Text flag;//文件来源标志
private Text secondPart;//除了链接键外的其他部分
public void setJoinKey(Text joinKey) {
this.joinKey = joinKey;
}
public void setFlag(Text flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public void setSecondPart(Text secondPart) {
this.secondPart = secondPart;
}
public Text getFlag() {
return flag;
}
public Text getSecondPart() {
return secondPart;
}
public Text getJoinKey() {
return joinKey;
}
public CombineValues() {
this.joinKey = new Text();
this.flag = new Text();
this.secondPart = new Text();
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
this.joinKey.write(out);
this.flag.write(out);
this.secondPart.write(out);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.joinKey.readFields(in);
this.flag.readFields(in);
this.secondPart.readFields(in);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CombineValues o) {
return this.joinKey.compareTo(o.getJoinKey());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "[flag="+this.flag.toString()+",joinKey="+this.joinKey.toString()+",secondPart="+this.secondPart.toString()+"]";
}
}
(2) map、reduce主体代码:
package com.mr.reduceSizeJoin;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @author zengzhaozheng
* 用途说明:
* reudce side join中的left outer join
* 左连接,两个文件分别代表2个表,连接字段table1的id字段和table2的cityID字段
* table1(左表):tb_dim_city(id int,name string,orderid int,city_code,is_show)
* tb_dim_city.dat文件内容,分隔符为"|":
* id name orderid city_code is_show
* 0 其他 9999 9999 0
* 1 长春 1 901 1
* 2 吉林 2 902 1
* 3 四平 3 903 1
* 4 松原 4 904 1
* 5 通化 5 905 1
* 6 辽源 6 906 1
* 7 白城 7 907 1
* 8 白山 8 908 1
* 9 延吉 9 909 1
* -------------------------风骚的分割线-------------------------------
* table2(右表):tb_user_profiles(userID int,userName string,network string,double flow,cityID int)
* tb_user_profiles.dat文件内容,分隔符为"|":
* userID network flow cityID
* 1 2G 123 1
* 2 3G 333 2
* 3 3G 555 1
* 4 2G 777 3
* 5 3G 666 4
*
* -------------------------风骚的分割线-------------------------------
* 结果:
* 1 长春 1 901 1 1 2G 123
* 1 长春 1 901 1 3 3G 555
* 2 吉林 2 902 1 2 3G 333
* 3 四平 3 903 1 4 2G 777
* 4 松原 4 904 1 5 3G 666
*/
public class ReduceSideJoin_LeftOuterJoin extends Configured implements Tool{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReduceSideJoin_LeftOuterJoin.class);
public static class LeftOutJoinMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, CombineValues> {
private CombineValues combineValues = new CombineValues();
private Text flag = new Text();
private Text joinKey = new Text();
private Text secondPart = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得文件输入路径
String pathName = ((FileSplit) context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString();
//数据来自tb_dim_city.dat文件,标志即为"0"
if(pathName.endsWith("tb_dim_city.dat")){
String[] valueItems = value.toString().split("\\|");
//过滤格式错误的记录
if(valueItems.length != 5){
return;
}
flag.set("0");
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
secondPart.set(valueItems[1]+"\t"+valueItems[2]+"\t"+valueItems[3]+"\t"+valueItems[4]);
combineValues.setFlag(flag);
combineValues.setJoinKey(joinKey);
combineValues.setSecondPart(secondPart);
context.write(combineValues.getJoinKey(), combineValues);
}//数据来自于tb_user_profiles.dat,标志即为"1"
else if(pathName.endsWith("tb_user_profiles.dat")){
String[] valueItems = value.toString().split("\\|");
//过滤格式错误的记录
if(valueItems.length != 4){
return;
}
flag.set("1");
joinKey.set(valueItems[3]);
secondPart.set(valueItems[0]+"\t"+valueItems[1]+"\t"+valueItems[2]);
combineValues.setFlag(flag);
combineValues.setJoinKey(joinKey);
combineValues.setSecondPart(secondPart);
context.write(combineValues.getJoinKey(), combineValues);
}
}
}
public static class LeftOutJoinReducer extends Reducer<Text, CombineValues, Text, Text> {
//存储一个分组中的左表信息
private ArrayList<Text> leftTable = new ArrayList<Text>();
//存储一个分组中的右表信息
private ArrayList<Text> rightTable = new ArrayList<Text>();
private Text secondPar = null;
private Text output = new Text();
/**
* 一个分组调用一次reduce函数
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<CombineValues> value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
leftTable.clear();
rightTable.clear();
/**
* 将分组中的元素按照文件分别进行存放
* 这种方法要注意的问题:
* 如果一个分组内的元素太多的话,可能会导致在reduce阶段出现OOM,
* 在处理分布式问题之前最好先了解数据的分布情况,根据不同的分布采取最
* 适当的处理方法,这样可以有效的防止导致OOM和数据过度倾斜问题。
*/
for(CombineValues cv : value){
secondPar = new Text(cv.getSecondPart().toString());
//左表tb_dim_city
if("0".equals(cv.getFlag().toString().trim())){
leftTable.add(secondPar);
}
//右表tb_user_profiles
else if("1".equals(cv.getFlag().toString().trim())){
rightTable.add(secondPar);
}
}
logger.info("tb_dim_city:"+leftTable.toString());
logger.info("tb_user_profiles:"+rightTable.toString());
for(Text leftPart : leftTable){
for(Text rightPart : rightTable){
output.set(leftPart+ "\t" + rightPart);
context.write(key, output);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf=getConf(); //获得配置文件对象
Job job=new Job(conf,"LeftOutJoinMR");
job.setJarByClass(ReduceSideJoin_LeftOuterJoin.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0])); //设置map输入文件路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //设置reduce输出文件路径
job.setMapperClass(LeftOutJoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(LeftOutJoinReducer.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); //设置文件输入格式
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);//使用默认的output格格式
//设置map的输出key和value类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(CombineValues.class);
//设置reduce的输出key和value类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
return job.isSuccessful()?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
try {
int returnCode = ToolRunner.run(new ReduceSideJoin_LeftOuterJoin(),args);
System.exit(returnCode);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
logger.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
其中具体的分析以及数据的输出输入请看代码中的注释已经写得比较清楚了,这里主要分析一下reduce join的一些不足。之所以会存在reduce join这种方式,我们可以很明显的看出原:因为整体数据被分割了,每个map task只处理一部分数据而不能够获取到所有需要的join字段,因此我们需要在讲join key作为reduce端的分组将所有join key相同的记录集中起来进行处理,所以reduce join这种方式就出现了。这种方式的缺点很明显就是会造成map和reduce端也就是shuffle阶段出现大量的数据传输,效率很低。
关于MapReduce多种join实现的示例分析就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。