жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жң¬зҜҮеҶ…е®№д»Ӣз»ҚдәҶвҖңmatlabжҖҺд№Ҳе®һзҺ°е°ҸиҪҰйҒҝи®©йҡңзўҚзү©вҖқзҡ„жңүе…ізҹҘиҜҶпјҢеңЁе®һйҷ…жЎҲдҫӢзҡ„ж“ҚдҪңиҝҮзЁӢдёӯпјҢдёҚе°‘дәәйғҪдјҡйҒҮеҲ°иҝҷж ·зҡ„еӣ°еўғпјҢжҺҘдёӢжқҘе°ұи®©е°Ҹзј–еёҰйўҶеӨ§е®¶еӯҰд№ дёҖдёӢеҰӮдҪ•еӨ„зҗҶиҝҷдәӣжғ…еҶөеҗ§пјҒеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶д»”з»Ҷйҳ…иҜ»пјҢиғҪеӨҹеӯҰжңүжүҖжҲҗпјҒ
еҲҶдёәдёүжӯҘпјҡ
иҪ¬жҚўдј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®
е°Ҷдј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®д»Һе°ҸиҪҰеқҗж Үзі»иҪ¬жҚўеҲ°дё–з•Ңеқҗж Үзі»
йҖҡиҝҮиҪ¬жҚўеҘҪзҡ„дј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®жұӮи§ЈйҒҝи®©иҝҗеҠЁеҸӮж•°
йҰ–е…Ҳжү“ејҖиҝҷдёӘж–Ү件
йҰ–е…ҲеңЁ
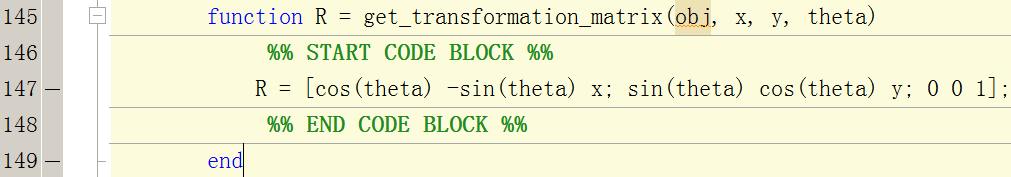
еҸ–еҫ—иҪ¬жҚўзҹ©йҳө
%% START CODE BLOCK %%
R = [cos(theta) -sin(theta) x; sin(theta) cos(theta) y; 0 0 1];
%% END CODE BLOCK %%
еңЁ
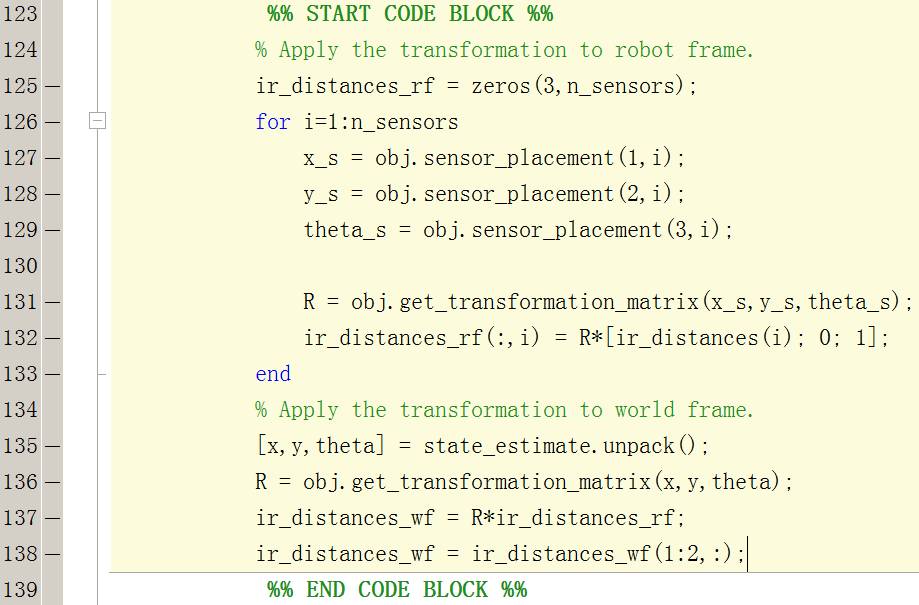
е®һзҺ°иҪ¬жҚўдј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®гҖҒе°Ҷдј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®д»Һе°ҸиҪҰеқҗж Үзі»иҪ¬жҚўеҲ°дё–з•Ңеқҗж Үзі»
%% START CODE BLOCK %%
% Apply the transformation to robot frame.
ir_distances_rf = zeros(3,n_sensors);
for i=1:n_sensors
x_s = obj.sensor_placement(1,i);
y_s = obj.sensor_placement(2,i);
theta_s = obj.sensor_placement(3,i);
R = obj.get_transformation_matrix(x_s,y_s,theta_s);
ir_distances_rf(:,i) = R*[ir_distances(i); 0; 1];
end
% Apply the transformation to world frame.
[x,y,theta] = state_estimate.unpack();
R = obj.get_transformation_matrix(x,y,theta);
ir_distances_wf = R*ir_distances_rf;
ir_distances_wf = ir_distances_wf(1:2,:);
%% END CODE BLOCK %%
然еҗҺеңЁ
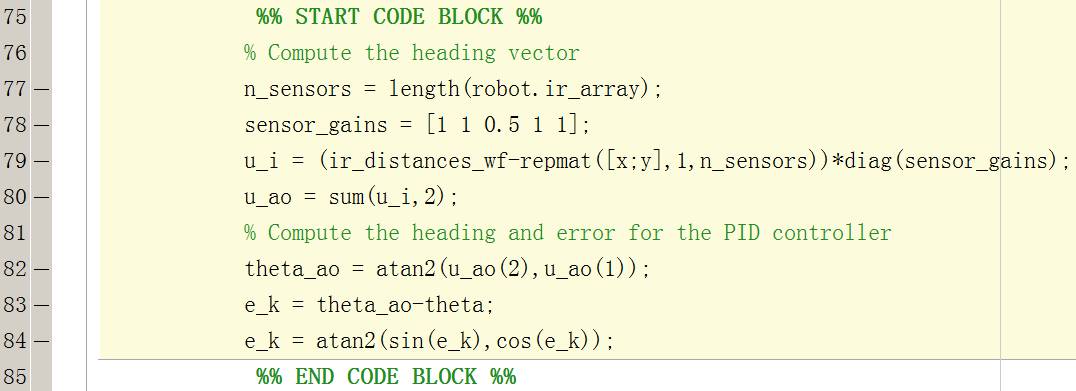
е®һзҺ°йҖҡиҝҮиҪ¬жҚўеҘҪзҡ„дј ж„ҹеҷЁж•°жҚ®жұӮи§ЈйҒҝи®©иҝҗеҠЁеҸӮж•°
%% START CODE BLOCK %%
% Compute the heading vector
n_sensors = length(robot.ir_array);
sensor_gains = [1 1 0.5 1 1];
u_i = (ir_distances_wf-repmat([x;y],1,n_sensors))*diag(sensor_gains);
u_ao = sum(u_i,2);
% Compute the heading and error for the PID controller
theta_ao = atan2(u_ao(2),u_ao(1));
e_k = theta_ao-theta;
e_k = atan2(sin(e_k),cos(e_k));
%% END CODE BLOCK %%
жңҖеҗҺиҝҗиЎҢ
вҖңmatlabжҖҺд№Ҳе®һзҺ°е°ҸиҪҰйҒҝи®©йҡңзўҚзү©вҖқзҡ„еҶ…е®№е°ұд»Ӣз»ҚеҲ°иҝҷйҮҢдәҶпјҢж„ҹи°ўеӨ§е®¶зҡ„йҳ…иҜ»гҖӮеҰӮжһңжғідәҶи§ЈжӣҙеӨҡиЎҢдёҡзӣёе…ізҡ„зҹҘиҜҶеҸҜд»Ҙе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘зҪ‘з«ҷпјҢе°Ҹзј–е°ҶдёәеӨ§е®¶иҫ“еҮәжӣҙеӨҡй«ҳиҙЁйҮҸзҡ„е®һз”Ёж–Үз« пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ