这篇文章主要讲解了“Spring中Bean的作用域与生命周期是什么”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Spring中Bean的作用域与生命周期是什么”吧!
通过Spring容器创建一个Bean的实例时,不仅可以完成Bean的实例化,还可以使用Bean的scope属性为bean设置作用域。
语法格式:<bean id="别名" scope="作用域" class="对应实现类">
作用域的种类:(sing)

singleton和prototype区别:(该两种比较常用)
① singleton单实例,prototype多实例
② 设置scope值是singleton时候,加载spring配置文件时候就会创建单实例对象
设置scope值是prototype时候,在加载spring配置文件时候暂时不会创建对象,在调用getBean方法时候才创建多实例对象
singleton作用域:
//Cat.java
public class Cat {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}配置文件beans5.xml
<bean id="cat" scope="singleton" class="com.jd.dao.Cat"> <property name="name" value="大橘"></property> </bean>
测试:
//Bean的作用域测试方法
@Test
public void catTest(){
//1.初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans5.xml");
//2.通过Spring容器获取Bean的实例
Cat cat1 = (Cat) applicationContext.getBean("cat");
Cat cat2 = (Cat) applicationContext.getBean("cat");
//3.输出获取的实例
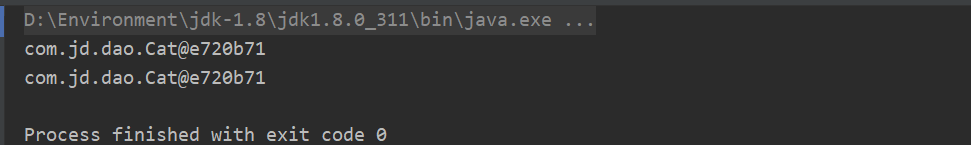
System.out.println(cat1);
System.out.println(cat2);
}
prototype作用域:
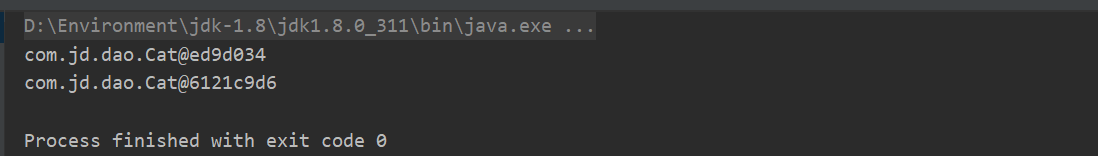
将配置文件beans5.xml中的scope属性改为prototype,再次运行测试:
<bean id="cat" scope="prototype" class="com.jd.dao.Cat"> <property name="name" value="大橘"></property> </bean>
3测试:
Bean从创建到销毁称为Bean的生命周期,大体上Bean的生命周期共有七步:
(1)通过无参构造器创建bean实例
(2)调用属性setter方法为bean的属性设置值
(3)把bean实例传递bean后置处理器的方法postProcessBeforeInitialization
(4)调用bean的初始化的方法(需要配置初始化的方法)
(5)把bean实例传递bean后置处理器的方法postProcessAfterInitialization
(6)获取使用已经创建的bean
(7)当容器关闭时候,调用bean的销毁的方法(需要配置销毁的方法)
注意:
① 初始化方法、销毁方法都需要在Bean中作为属性手动配置;
② 只有singleton作用域的Bean才会执行销毁方法;
(1)普通Java Bean:Cat.java
public class Cat {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("第二步:调用属性setter方法为bean的属性设置值");
}
public Cat(){
System.out.println("第一步;通过无参构造器创建bean实例");
}
//初始化方法(在配置文件中配置实现调用)
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("第四步:调用bean的初始化的方法");
}
//销毁方法(在配置文件中配置实现调用)
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("第七步:当容器关闭时候,调用bean的销毁的方法");
}
}(2)myBeanPostProcessor实现BeanPostProcessor接口,实现后置处理器:myBeanPostProcessor.java
(spring中的AOP就是通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口实现的)
//myBeanPostProcessor实现BeanPostProcessor接口,实现后置处理器
public class myBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第三步:把bean实例传递bean后置处理器的方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:把bean实例传递bean后置处理器的方法");
return bean;
}
}(3)配置文件:beans5.xml
<!--scope属性必须设置为singleton,否则创建的Bean不会被销毁--> <!--init-method属性配置初始化方法,destroy-method属性销毁方法--> <bean id="cat" scope="singleton" class="com.jd.dao.Cat" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"> <property name="name" value="大橘"></property> </bean> <!--配置后置处理器,为当前配置文件中的所有bean添加后置处理器的处理--> <bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.jd.dao.myBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
(4)测试
@Test
public void catTest(){
//1.初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans5.xml");
//2.通过Spring容器获取Bean的实例
Cat cat = (Cat) applicationContext.getBean("cat");
//3.输出获取的实例
System.out.println("第六步:获取创建Bean实例"+cat);
//4.手动关闭
applicationContext.close();
}
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Spring中Bean的作用域与生命周期是什么”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Spring中Bean的作用域与生命周期是什么这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。