一、简介
就应用来说,map已经是STL标准库的成员,而hash_map暂时还未进入标准库,是扩展ext中的一个功能,但也是非常常用并且非常重要的库。
二、简单对比
首先,要说的是这两种数据结构的都提供了KEY-VALUE的存储和查找的功能。但是实现是不一样的,map是用的红黑树,查询时间复杂度为log(n)。而hash_map是用的哈希表,查询时间复杂度理论上可以是常数,但是消耗内存大,是一种以存储换时间的方法。
树查找,在总查找效率上比不上hash表,但是它很稳定,它的算法复杂度不会出现波动。在一次查找中,你可以断定它最坏的情况下其复杂度不会超过O(log2N)。而hash表就不一样,是O(1),还是O(N),或者在其之间,你并不能把握。
三、hash_map的使用
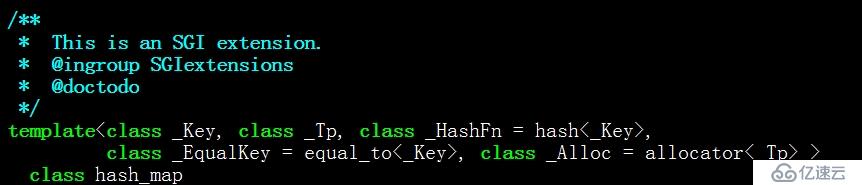
可见,如果定义完整的hash_map,需要提供<key类型,value类型,哈希函数,key相等判断函数,value类型内存分配器>等5个模板参数,由于后三个都有默认值,所以一般我们只需要提供前两个。
1> 定义__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> myHashMap不会出错,然而一旦对myHashMap进行操作,就会出现编译错误“instantiated from here”,这是因为gnu版本的hash_map只实现了有限的几个hash模板函数(见第三个模板参数,这些函数在hash_fun.h中),而这些函数里包括hash<const char*>,但是不包括hash<std::string>的实例化。解决办法是定义哈希表前自己特化一个实例,这样编译器就知道调用这个函数了。
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}2> 第四个参数key相等判断函数的意义
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int> myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int>::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
return 0;
}你会发现,虽然name1和name2都是zhu,但是插入了name1,用name2去查找时,还是查无结果。这是涉及到第四个模板参数,判断key相等,默认的是std::equal_to,而这个函数的定义是用operator==来进行判断的,指针的相等当然就是地址一样了,而name1和name2的地址显然不同。解决办法是用自己指定的函数模板替代默认的。
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ext/hash_map>
#include <backward/hash_fun.h>
using namespace std;
template <class _Tp>
struct my_equal_to : public binary_function<_Tp, _Tp, bool>
{
bool operator()(const _Tp& __x, const _Tp& __y) const
{ return strcmp(__x, __y) == 0; }
};
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> > myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> >::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
else
cout << it->second << endl;
return 0;
}用刚刚特化的hash_map<string, int>就是可以找到的,因为string重载了operator==操作符。
编译使用-Wno-deprecated选项,不然会有backward_warning.h头文件里的告警。
四、肤浅的对比测试(map,系统hash函数的hash_map及自写hash函数的hash_map)
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ cat /tmp/name.txt | wc -l
25848136
#从现有的游戏数据库里拉了561916个角色名(里面本来就有重复的),然后重复追加了几次,变成了
#2584万行的数据1.系统hash函数的hash_map实现
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
//特化hash函数的string版本
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}
//计算当前时间
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp; //存放每行的临时字符串
int i = 0; //统计总个数
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime(); //从这里开始计时
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime(); //计时结束
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#编译
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 3.cpp -o hashMap#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
struct strHash{
size_t operator()(const string& str) const
{
unsigned long __h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < str.size() ; i ++)
__h = 107*__h + str[i];
return size_t(__h);
}
};
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int, strHash> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#编译
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 4.cpp -o strhashMap#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime (&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#编译
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ 2.cpp -o map[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./hashMap #7秒
2015-11-06 16:25:41
2015-11-06 16:25:48
459256
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./strhashMap #8秒,和上面的相差无几
2015-11-06 16:25:50
2015-11-06 16:25:58
459256
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./map #26秒
2015-11-06 16:26:02
2015-11-06 16:26:28
459256六、注意hash_map死循环
这个问题简单说来,就是gnu的实现是,内部有个_M_Cur指针指示当前位置A,每次计算operator++,都用当前位置的key调用hash函数计算下一个位置B,如果key传入hash_map以后,又在外部将其内容破坏,导致hash函数计算后的B位置在A位置之前,那么从B到达A以后,又会跳回B,形成B-A区间的死循环。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int> hashMap;
char name[10] = "zhu";
hashMap.insert(pair<char *, int>(name, 1));
strncpy(name, "wang", 10); //在外部改变了已经传入hash_map中的key,导致死循环
for (__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int>::iterator it = hashMap.begin(); it != hashMap.end(); ++it)
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。