本篇内容介绍了“R语言怎么实现散点图组合频率分布图”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
部分数据如下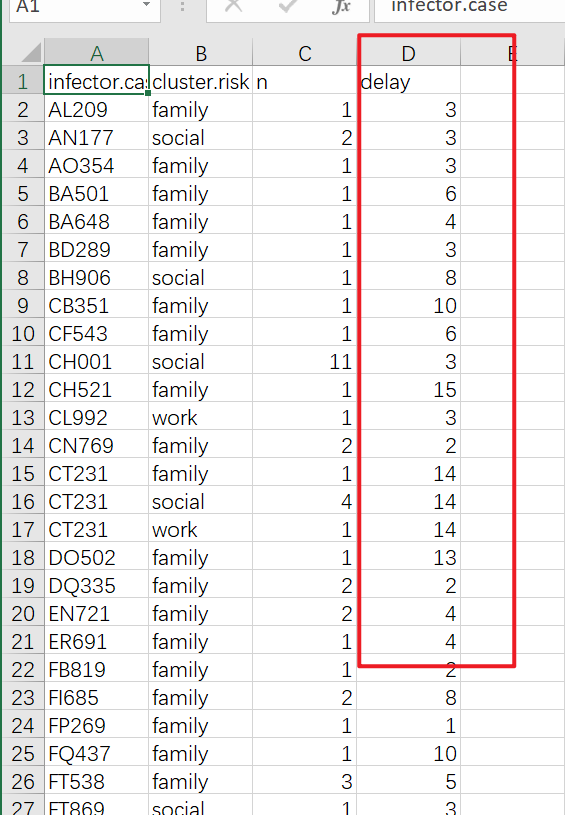
做图用到的是最后一列数据
df1<-read.csv("example1.csv",header=T)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(df1) +
geom_histogram(aes(x = delay,y=..density..),
fill = '#dedede', colour = "black",
binwidth = 1) +
scale_y_continuous("Frequency", expand = c(0,0), limits = c(0,0.20)) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-isolation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27),
breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme(#aspect.ratio = 2,
legend.position = 'none')
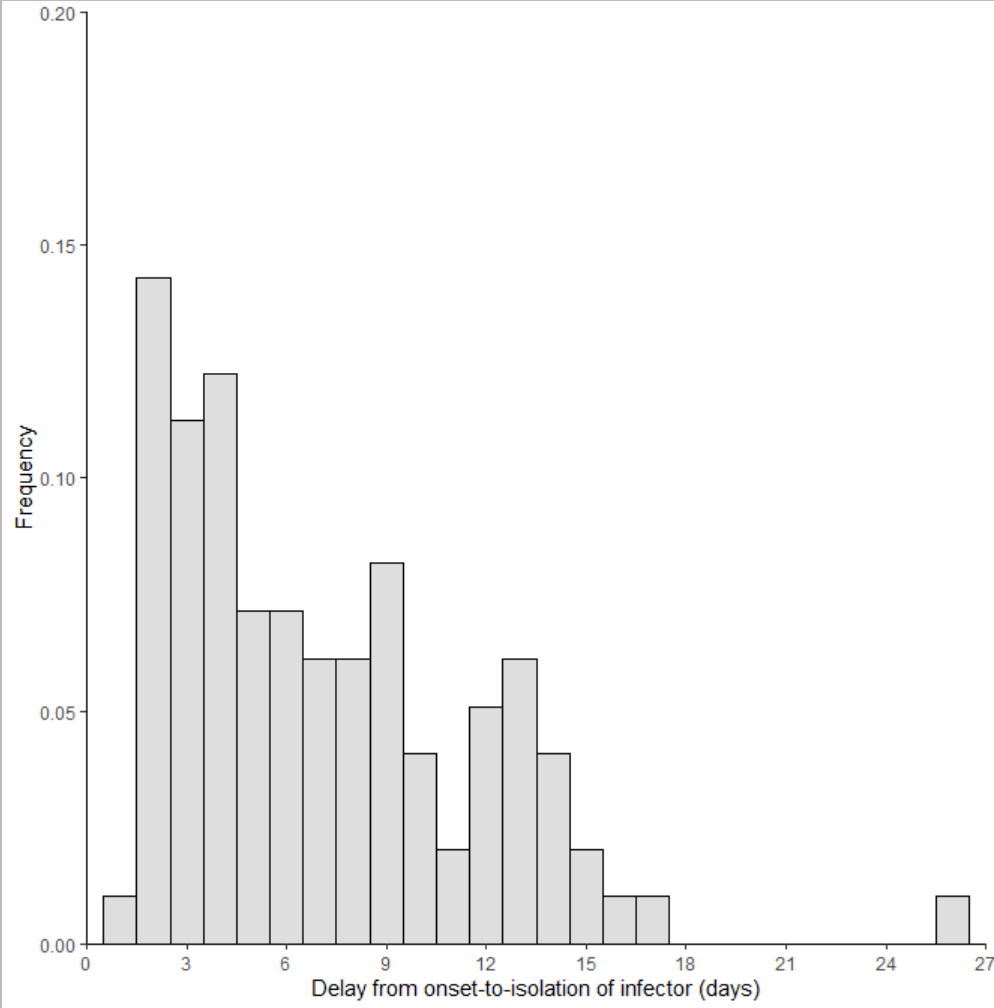
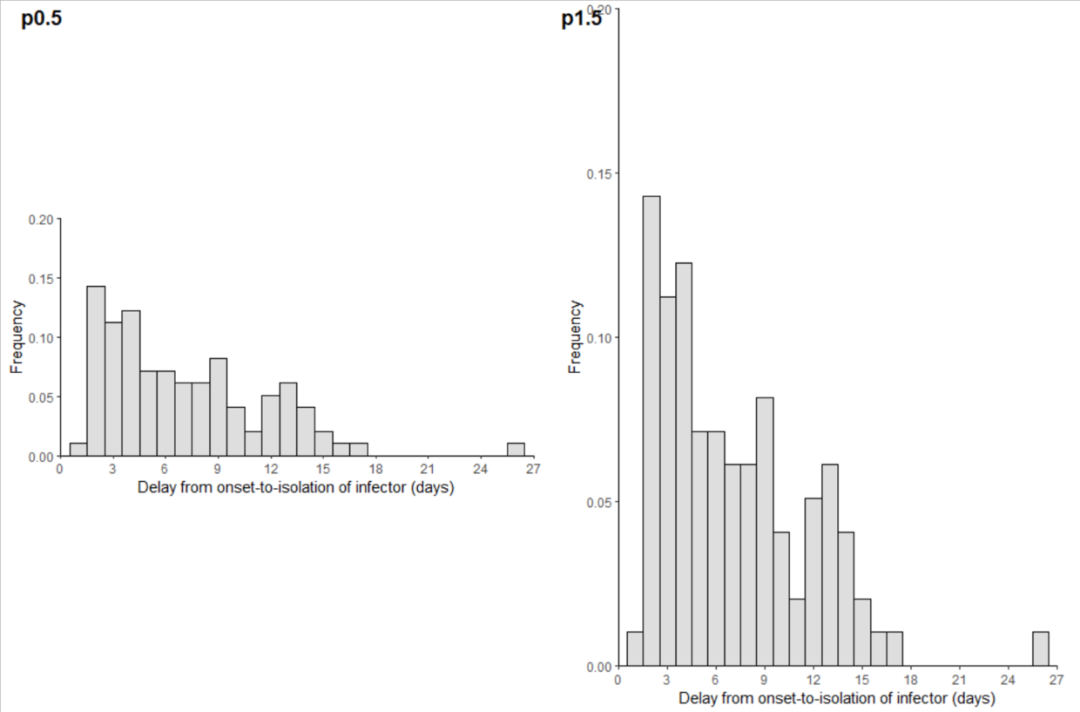
这里新学到的知识点是theme()函数里的aspect.ratio参数,这个参数可以控制整幅图占比,如果是0到1之间就是纵向的压缩,如果是1到2之间就是纵向的压缩,我们分别设置0.5和1.5看下效果
p0.5<-ggplot(df1) +
geom_histogram(aes(x = delay,y=..density..),
fill = '#dedede', colour = "black",
binwidth = 1) +
scale_y_continuous("Frequency", expand = c(0,0), limits = c(0,0.20)) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-isolation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27),
breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme(aspect.ratio = 0.5,
legend.position = 'none')
p0.5
p1.5<-ggplot(df1) +
geom_histogram(aes(x = delay,y=..density..),
fill = '#dedede', colour = "black",
binwidth = 1) +
scale_y_continuous("Frequency", expand = c(0,0), limits = c(0,0.20)) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-isolation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27),
breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme(aspect.ratio = 1.5,
legend.position = 'none')
cowplot::plot_grid(p0.5,p1.5,labels = c("p0.5","p1.5"))
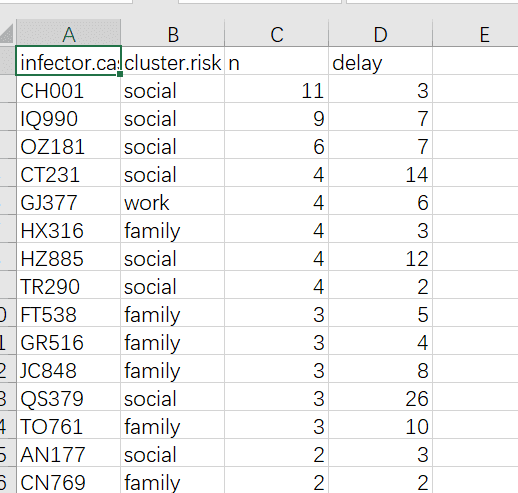
散点图的部分数据如下
df2<-read.csv("example2.csv",header=T)
ggplot(df2) +
geom_smooth(method = lm, aes(x=delay, y = n), color = "black", alpha = 0.1, size = 0.7) +
geom_jitter(aes(x = delay, y = n, colour = cluster.risk), height = 0.3, width = 0.3) +
scale_y_continuous("Secondary Cases / Infector", breaks = 1:11) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-confirmation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27), breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme(aspect.ratio = 1, legend.position = c(0.85, 0.85), legend.title = element_blank()) #colours are modified custom in post
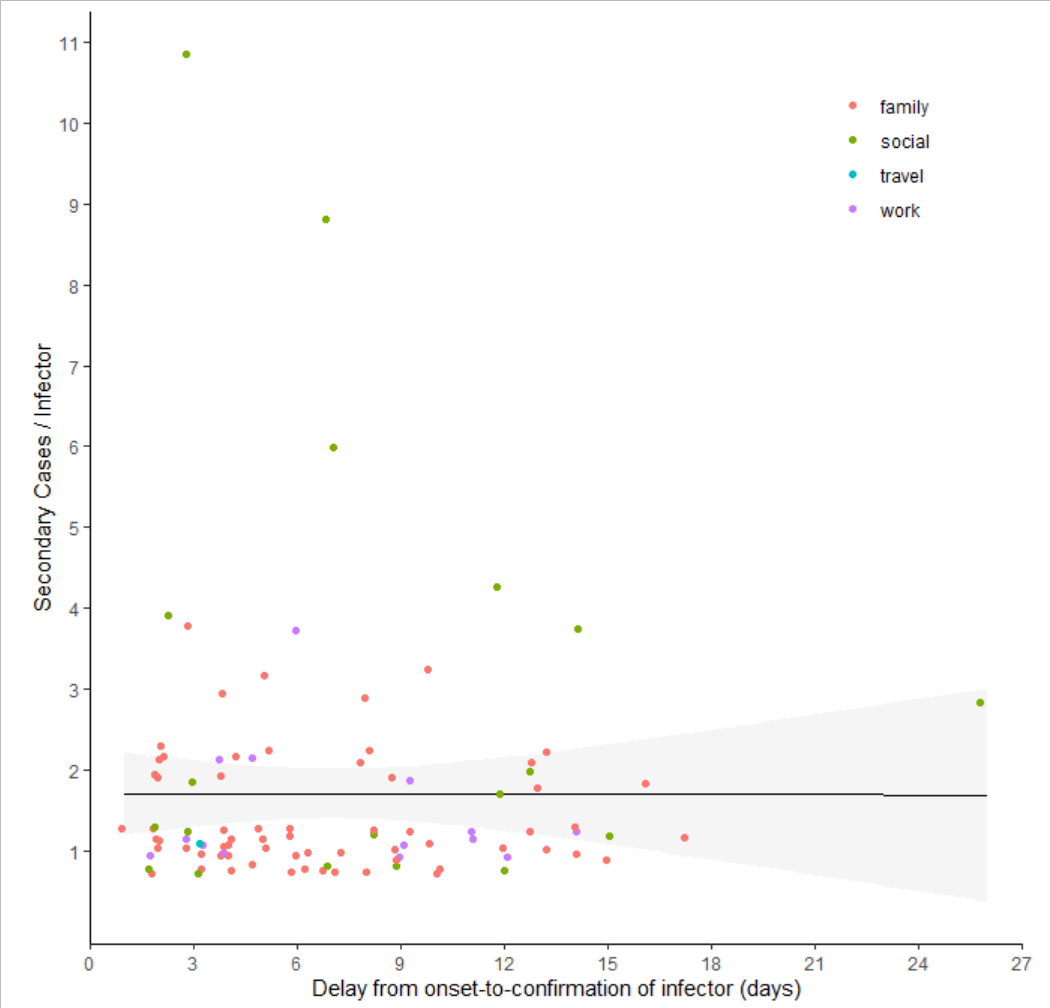
这里需要注意的是散点图他用到的函数是geom_jitter(),而没有用geom_point(),这两个函数的区别是如果两个点的坐标是一样的geom_jitter()函数也会将两个点分开,而geom_point()函数会将两个点重叠的画到一起
p1<-ggplot(df1) +
geom_histogram(aes(x = delay,y=..density..),
fill = '#dedede', colour = "black",
binwidth = 1) +
scale_y_continuous("Frequency", expand = c(0,0), limits = c(0,0.20)) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-isolation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27),
breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme(#aspect.ratio = 0.5,
legend.position = 'none')
p2<-ggplot(df2) +
geom_smooth(method = lm, aes(x=delay, y = n), color = "black", alpha = 0.1, size = 0.7) +
geom_jitter(aes(x = delay, y = n, colour = cluster.risk), height = 0.3, width = 0.3) +
scale_y_continuous("Secondary Cases / Infector", breaks = 1:11) +
scale_x_continuous("Delay from onset-to-confirmation of infector (days)",
expand = c(0,0),
limits = c(0,27), breaks = seq(0,27, by = 3)) +
theme_classic() +
theme( legend.position = c(0.85, 0.85),
legend.title = element_blank()) #colours are modified custom in post
library(aplot)
p2%>%
insert_top(p1,height = 0.3)
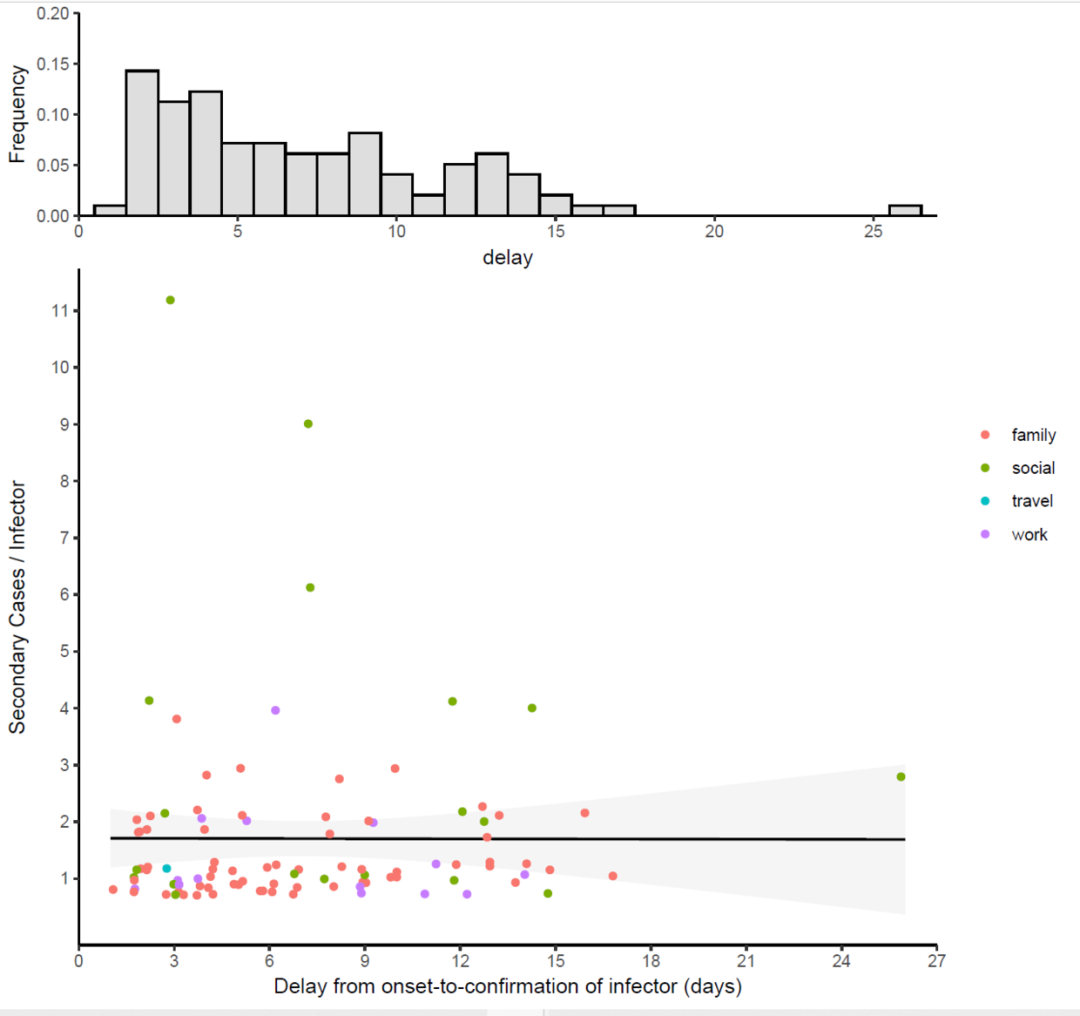
“R语言怎么实现散点图组合频率分布图”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。