这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关python怎么用plotly实现绘制局部放大图,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
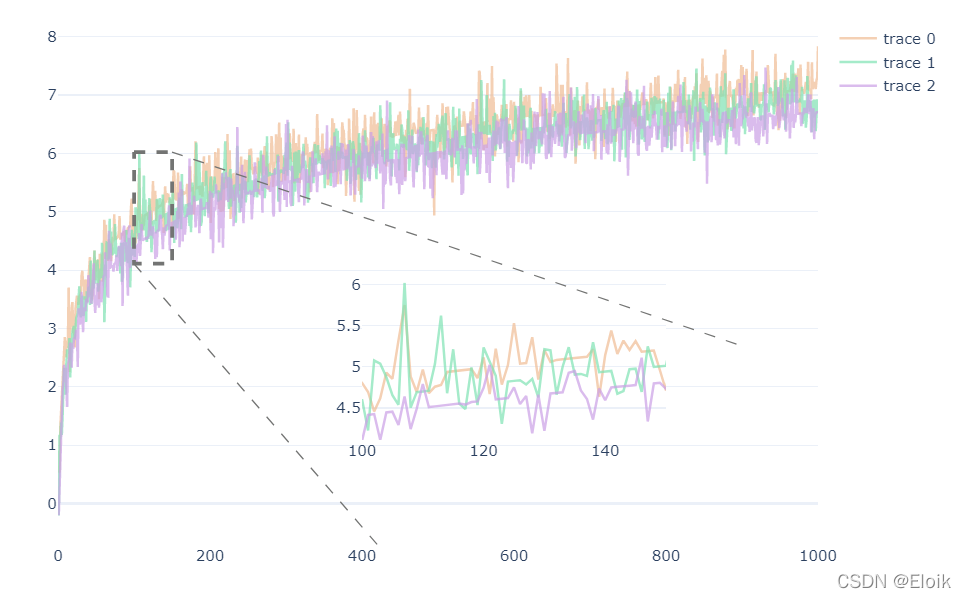
在绘图区域插入一个嵌入图,嵌入图与原图的绘画保持一致,通过限制嵌入图的x轴和y轴的显示范围,达到缩放的效果,并在原图上绘画一个矩形框,以凸显缩放的区域,最后通过两条直线凸显缩放关系。
import plotly.io as pio import plotly.graph_objects as go import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 设置plotly默认主题,白色主题 pio.templates.default = 'plotly_white'
# x坐标 x = np.arange(1, 1001) # 生成y轴数据,并添加随机波动 y1 = np.log(x) indexs = np.random.randint(0, 1000, 800) for index in indexs: y1[index] += np.random.rand() - 0.5 y1 = y1 + 0.2 y2 = np.log(x) indexs = np.random.randint(0, 1000, 800) for index in indexs: y2[index] += np.random.rand() - 0.5 y3 = np.log(x) indexs = np.random.randint(0, 1000, 800) for index in indexs: y3[index] += np.random.rand() - 0.5 y3 = y3 - 0.2
class LocalZoomPlot:
def __init__(self, x, y, colors, x_range, scale=0.):
"""
:param x: x轴坐标,列表类型
:param y: y轴坐标,二维列表类型,例如 [y1, y2, y3]
:param colors: 每个曲线的颜色,必须与 len(y) 相等
:param x_range: 需要缩放区域的x轴范围
:param scale: 详见 getRangeMinMaxValue 函数
"""
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.colors = colors
self.x_range = x_range
self.y_range = self.getRangeMinMaxValue(x_range, scale)
def getRangeMinMaxValue(self, x_range, scale=0.):
"""
获取指定x轴范围内,所有y数据的最大值和最小值
:param x_range: 期望局部放大的x轴范围
:param scale: 将最大值和最小值向两侧延伸一定距离
"""
min_value = np.min([np.min(arr[x_range[0]:x_range[1]]) for arr in self.y])
max_value = np.max([np.max(arr[x_range[0]:x_range[1]]) for arr in self.y])
# 按一定比例缩放
min_value = min_value - (max_value - min_value) * scale
max_value = max_value + (max_value - min_value) * scale
# 返回缩放后的结果
return min_value, max_value
def originPlot(self, fig, **kwargs):
"""
根据 y 数据绘制初始折线图
:param fig: go.Figure实例
"""
fig.add_traces([
go.Scatter(x=self.x, y=arr, opacity=0.7, marker_color=self.colors[i], **kwargs)
for i, arr in enumerate(self.y)
])
return fig
def insetPlot(self, fig, inset_axes):
"""
在原始图像上插入嵌入图
:param fig: go.Figure对象实例
:param inset_axes: 嵌入图的位置和大小 [左下角的x轴位置, 左下角的y轴位置, 宽度, 高度]
所有坐标都是绝对坐标(0~1之间)
"""
# 使用创建子图中的嵌入图参数,创建一个嵌入图
fig = fig.set_subplots(insets=[dict(
type='xy',
l=inset_axes[0], b=inset_axes[1],
w=inset_axes[2], h=inset_axes[3],
)])
# 嵌入图与原始图的绘画一致,需要指定 xaxis 和 yaxis 参数确保是在嵌入图上绘画的
fig = self.originPlot(fig, xaxis='x2', yaxis='y2', showlegend=False)
# 将嵌入图的坐标轴范围限定在指定范围
fig.update_layout(
xaxis2=dict(range=self.x_range),
yaxis2=dict(range=self.y_range)
)
return fig
def rectOriginArea(self, fig):
"""
将放大的区域框起来
:param fig: go.Figure实例
"""
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(
# 从左上角开始,顺时针连线
x=np.array(self.x_range)[[0, 1, 1, 0, 0]],
y=np.array(self.y_range)[[1, 1, 0, 0, 1]],
mode='lines',
line={'color': '#737473', 'dash': 'dash', 'width': 3},
showlegend=False
))
return fig
def addConnectLine(self, fig, area_point_num, point):
"""
从放大区域指定点连线
:param fig: go.Figure实例
:param area_point_num: 放大区域的锚点,例如:(0, 0)表示放大区域的左下角坐标,(0, 1)表示左上角坐标,
(1, 0)表示右下角坐标,(1, 1)表示右上角坐标,只能取这四种情况
:param point: 要进行连线的另一个点,通常位于嵌入图附近,根据美观程度自行指定
"""
fig.add_shape(type='line',
x0=self.x_range[area_point_num[0]],
y0=self.y_range[area_point_num[1]],
x1=point[0], y1=point[1],
line={'color': '#737473', 'dash': 'dash', 'width': 1},
)
return figplot = LocalZoomPlot(x, [y1, y2, y3], ['#f0bc94', '#7fe2b3', '#cba0e6'], (100, 150), 0.) fig = go.Figure() fig = plot.originPlot(fig) fig = plot.insetPlot(fig, (0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 0.3)) fig = plot.rectOriginArea(fig) fig = plot.addConnectLine(fig, (0, 0), (420, -0.7)) fig = plot.addConnectLine(fig, (1, 1), (900, 2.7)) # 额外对图片进行设置 fig.update_layout( width=800, height=600, xaxis=dict( rangemode='tozero', showgrid=False, zeroline=False, ), xaxis2=dict( showgrid=False, zeroline=False ), ) fig.show()
关于“python怎么用plotly实现绘制局部放大图”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。